mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- possession and overseas territory of United Kingdom in the Southern Atlantic
- other names: "SGSSI", "Southern Antilles"
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Other Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1908,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






since 1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 1999,
Flag of the Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1992–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



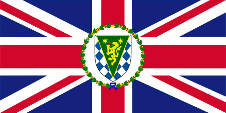
1992–1999,
Flag of the Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




spread variants, possibly historical

1992–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



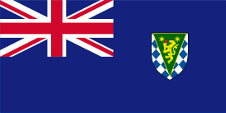
1992–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The Union Jack points to the connexions to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other.
Since 1999, the complete coat of arms of the islands has appeared on the flag of the authorities (Blue Ensign) instead of the badge introduced in 1992. In the literature and on the internet, there are a few variants of this flag. Only the shield is shown on the flag, sometimes with and sometimes without a white disc. This is possibly due to the fact that the flag of the Commissioner between 1992 and 1999 actually only showed the escutcheon, which was transferred to the flag of the authorities.
In many British possessions and partly also in the Commonwealth, there has been and still is a trend for the Blue Ensign, i.e. the actual sea flag of the authorities with the local badge (insignia), to be used by authorities also on land or even by civilians. In some cases, this has been done officially by unilaterally creating facts. However, this is usually only tolerated under protest. Actually, the individual citizen represents the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, visible on land by the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag", at sea by the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of the colony were allowed to use their own Red Ensign with the badge of the colony at sea, which often led to the use of these Red Ensigns on land instead of the Union Flag, even with other local badges, for example in some Canadian provinces. Similarly, in some British possessions, Red Ensigns were created and used by citizens on their own authority and without permission.
The flag of the Commissioner is a standard-design of older styling, for all Governors, Lieutenant-Governors, Commissioners, High-Commissioners and other administering government officials, provided no newer designs are in use. Within the wreath the respective badge or coat of arms is always positioned. The Commissioner of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Inseln is at the same time the governor of the Falkland Islands. His flag is only in use if he visits the islands.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


since 1992,
Coat of arms of South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

1992–1999,
Badge of South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

The coat of arms of the country shows a shield with a white-blue diagonal chessboard-pattern. On it a golden bordered green triangle with a golden lion with a torch and two golden stars. The shield is based on a undercoat from planks, grass and ice. Shield-supporters are a sea-elephant and a penguin. Above the blazon a helmet with a white-blue torus and on it a reindeer which stands on cliffs. Quite below a ribbon with the motto of the islands. The motto is: "Leo Terram Propriam Protegat", what means something like "Let the Lion protect its own Land". The golden lion in the coat of arms is the heraldic symbol of United Kingdom, the torch points out for the scientific research on the islands and the both stars stand for the both archipelagos the country consists of. The penguin, the sea-elephant and the reindeer are a hint for the fauna of the country.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

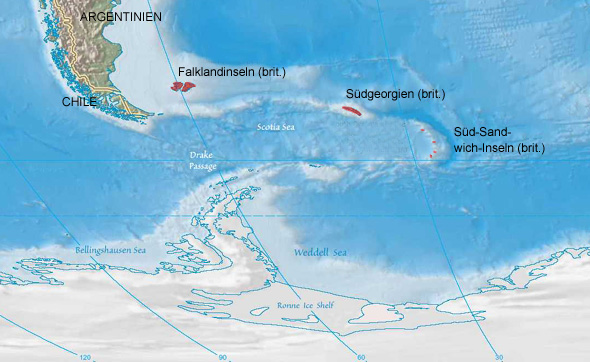
Location:
Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
Map of the country:
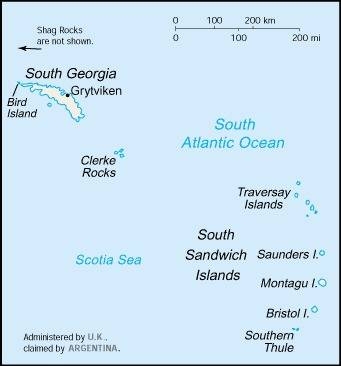
Source: CIA World Factbook
Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
Reseach stations and former settlements
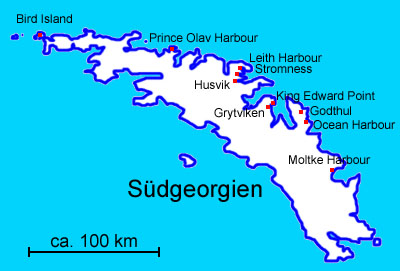
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 1.570 square miles, thereof South Georgia 1.450 sq.mi., South Sandwich Islands 120 sq.mi.
Inhabitants: There is no permanent human population on South Georgia. There are 2 Government Officers and spouses, up to 25 British Antarctic Survey personnel at 2 research stations and up to 4 Museum staff in the summer months.
Density of Population: 0,02 inh./sq.mi.
Main place: King Edward Point/Grytviken
Seat of administration: Stanley (Falkland Islands)
official Language: English
Currency 1: Pound Sterling (£) = 100 Pence
Currency 2: Falkland-Islands-Pound (F.I.-£, FKP) = 100 Pence
Time Zone: GMT – 2 h
Source: GSGSSI,
Wikipedia (D)

1675 · the English seafarer Anthony de la Roche discovers the island of South Georgia, which first of all became noted as Roche Island but its position however fell in oblivion
1775 · the English seafarer James Cook discoveres South Georgia again and discoveres the South Sandwich Islands and claims them for United Kingdom
1819 · the Russian seafarer Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen discoveres further islands of the South Sandwich Archipelago
1819 · the South Shetland Islands (888 sq.mi., uninhabited) become appropriated by United Kingdom
1821 · the South Orkney Islands (256 sq.mi., uninhabited) become appropriated by United Kingdom
1882 · construction of the German research station Moltke (Moltke Harbour) in the Royal Bay in the southeast of the island
1904 · foundation of the whaler housing estate Grytviken by Carl Anton Larsen
1908 · United Kingdom officially appropriates South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands as dependenceies of the Falkland Islands, the South Shetland Islands and the South Orkney Islands become further dependenceies of the Falkland Islands
1908 · foundation of the whaler housing estate Godthul
1909 · foundation of the whaler housing estates Leith Harbour and Ocean Harbour
1909 · foundation of King Edward Point as administrative center near Grytviken
1910 · foundation of the whaler housing estate Husvik
1912 · foundation of the whaler housing estate Stromness
1916 · foundation of the whaler housing estate Prince Olav Harbour
1916 · the polar researcher Ernest Henry Shackleton visits Grytviken
1920 · the whaler housing estate Ocean Harbour becomes given up and abandoned
1922 · the polar researcher Ernest Henry Shackleton dies in Grytviken and was buried there
1927 · Argentina claims South Georgia
1929 · the whaler housing estate Godthul becomes given up and abandoned
1931 · the whaler housing estate Stromness becomes given up and abandoned
1934 · the whaler housing estate Prince Olav Harbour becomes given up and abandoned
1938 · Argentina claims the South Sandwich Islands
1949 · King Edward Point becomes extended as scientific research station
1955–1956 · Argentina occupies Thule Island, the most southern island of the South Sandwich Islands and operates over one summer the military base Teniente Esquivel
1958 · United Kingdom builds the research station of Bird Island in the north of South Georgia
1960 · the whaler housing estate Husvik becomes given up and abandoned
1960–1961 · the smallholding of Stromness becomes operated as repairing shipyard
1962 · the South Shetland Islands and the die South Orkney Islands become administratively separated from the Falkland Islands and affiliated to the British Antarctic Territory
1965 · the whaler housing estate Leith Harbour becomes given up and abandoned
1965 · the place Grytviken becomes given up as whaler station
1976 · Argentina occupies again Thule Island and establishes the military base Corbeta Uruguay
19th of March 1982 · occupation of the abandoned whaler station Leith Harbour by Argentinian troops
3rd of April 1982 · occupation of Grytviken by Argentinian troops
25th of April 1982 · re-conquest of South Georgia by British troops on the occasion the Falkland War, station of a British garrison in King Edward Point
20th of June 1982 · Argentina quits the military base Corbeta Uruguay
3rd of October 1985 · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands become administratively separated from the Falkland Islands and represent from now on an own administration unit
1993 · extension of the 12 mile fishery zone to 200 miles around the islands
1995 · Argentina cancels the power for the achievement of its interests in South Georgia
21st of March 2001 · the British garrison withdraws from King Edward Point
Source:
1) Wikipedia (EN),
2) Wikipedia (EN),
Wikipedia (DE)

When South Georgia was discovered in 1675 it was initially called after the name of its discoverer. The name was "Roche Island". As James Cook re-discovered the island in 1775 he named it to honour the British King George III. "Isle of Georgia". James Cook also discovered in the year 1775 the most of the 750 miles from South Georgia distant and uninhabited South Sandwich Islands. He named them to honour the 4th Earl of Sandwich, the First Lord of the Admirality "Sandwich Islands". Later was added the word "South" to distinguish them from Hawaii, which at that time was called Sandwich Islands too.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)


![]()




























