mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- former Emirate, Sultanate and Kingdom in Central Arabia
- today's central part of Saudi Arabia
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
A special feature of the flags on this website is an inscription with Arabic script. In European understanding, any inscription on a flag is considered to be on the front of the flag, the writing always running from left to right, so that the respective inscription starts next to the pole on the left and continues to the right - towards the waving end of the flag. The Arabic script, however, is read from right to left. The European way of understanding at these things should not be applied to flags with Arabic inscriptions, because if the pole were on the left, the Arabic writing would run from the waving end towards the pole, which is not allowed. Sometimes this argument is reinforced by illustrations, e.g. a sword with the tip of the sword pointing towards the end of the shahada. If one wants to show this correctly on this type of flag, the writing must run away from the mast, Arabic from right to left, the sword then also pointing from right to left, which means that the mast must necessarily be on the right. In order to use this type of flag correctly, two front sides must be sewn against each other, a mirror-inverted print-through would not be appropriate.


1727–ca.1750,
Sheikhdom of Diriyah,
Flag of the Sheikhdom of Diriyah,
Source, by: World Statesmen





ca.1750–1818,
Emirate of Diriyah,
Flag of the Emirate of Diriyah,
Source, by:
World Statesmen





ca.1824–1887,
Emirate of Nejd,
Flag of the Emirate of Nejd,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1836–1921,
Emirate of Jebel Shammar,
Flagge des Emirats Dschebel Shammar,
Source, by:
World Statesmen





1902–1913,
Emirate of Nejd,
Flag of the Emirate of Nejd,
Source, by:
World Statesmen





1913–1921,
Emirate of Nejd,
Flag of the Emirate of Nejd,
Source, by:
World Statesmen





1921–1926,
Sultanate of Nejd,
Flag of the Sultanate of Nejd,
Source, by:
World Statesmen





1926–1932,
Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd,
Flag of the Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), SALEM,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




The flag of the Emirate of Al-Darija was initially probably single-coloured red, an in this region usual and entirely far spreaded design of a flag. In the 18th century established Ibn Abd al-Wahhab (1720–1792) an Islamic-Sunnitic movement, which was later named by him – the Wahabites. He missioned in Nejd, and got since 1745 big influence in the familiy of Saud, the rulers in the Sheikhdom of Al-Darija. This family took completely over the symbolism of the Wahabites (the colour green, the Shahada and temporary the half-moon) and that symbolism became in the 20th century to the heraldry of the Kingdom of Nejd and later of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia too. The Shahada is the credo of the Islam: "Allah il Allah, wa Muhammad rasul Allah" → "There is no God but God; and Mohammed is His messenger". In 1887 the Emirate of Nedjd was conquered by the Shammar tribes. When the Emirate of Nedjd was re-established in 1902, the old flag was re-introduced. Between 1926 and 1932, another Arabic inscription was displayed below the sword on the flag. It can be translated as follows: "Victory with God, Islamization of all countries". The colour green was the colour of the coat of the Prophet Mohammed. In that times (even in Europe) it was sometimes usual to use garments as flag. In this way as well with the coat of Mohammed. The colour of the coat became in this way very quick to colour and flag of the Islam, and especially to the colour of the Fatimids, an Ismailic-Shiite dynasty of Califs, which have their roots in the fourth Calif Ali, and Fatima, the daughter of Mohammed. The sword was added to the flag in 1913 and refers to the founder of the state of Saudi Arabia Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. (1880–1953). It represents the military triumphs of the Islam, of the Saud family and of the Wahabites. It stands for justice and honesty.
Source: Wikipedia (EN), Die Welt der Flaggen, Volker Preuß

The Arabian Peninsula about 1920, interactive Map:
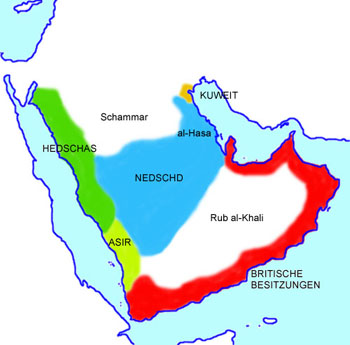
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: ca. ca. 536.795 square miles
Inhabitants: 3.500.000 (nowadays)
Capital: Riad (Ar Rijad)
Source:
Encyclopédie Universelle

15th century · evolution of the Sheikhdom of Al-Darija under the dynasty of the Saud near Riad
1744 · Emir Mohammed Ibn Saud of Al-Darija (1726–1766) accomodates the strict religious Sheik Mohammed Ibn Abd al-Wahhab (1720–1792, al-Wahhab is the founder of the religious movement of the Wahabits), that gains big influence onto Emir Mohammed Ibn Saud, Al-Darija becomes an emirate and Wahabi state
1773 · conquest of Riad by the Saudi-Wahabites
1788 · whole central Arabia is in the hands of the Saudi-Wahabites
1801 · Saudi troops conquer Karbala City
1806 · Saudi troops conquer Makkah City
1812 · Mohammed Ali, the Ottoman Viceroy of Egypt, begins to counter the Wahabites
1818 · subjection of the Saudi Wahabites-State by Mohammed Ali
1824 · the Saudis conquer Riyadh and found the Emirate of Nejd
1887 · the Emirate of Nejd is conquered by the Shammar tribes
1902 · the Saudis re-conquer Riyadh and found the Emirate of Nejd again
1891 · rebellion of the Saud against the Shammar, defeat, escape of the Saud family to Kuwait
1902 · Emir Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. succeeds in the conquest of Riad with support by the Emir of Kuwait, union of the tribes of Nejd under the Sauds
1909 · the Ottoman Empire recognizes the reign of Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. in Nejd
1913 · Saudi troops conquer the Ottoman coastal province of Al-Hasa at the Persian Golf
1915 · United Kingdom recognizes the reign of Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. in Nejd, peace agreement between Nejd and United Kingdom
1921 · Saudi troops conquer Shammar
22nd of August 1921 · proclamation of the Sultanate of Nejd, under Sultan Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III.
1921–1925 · Saudi troops conquer Hejaz
1922 · United Kingdom disclaims its zone of influence in the Rub al-Khali desert
2nd of December 1922 · establishment of a Neutral Zone between Nejd and Kuwait, as well as between Nejd and Iraq
1926 · frontier treaty with Iraq and Trans Jordan
1926 · coronation of Sultan Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. to the King of Hejaz
19th of January 1927 · coronation of Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III. to the King of Nejd and Hejaz
18th of September 1932 · formation of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by unification of the Kingdom of Hejaz with the Kingdom of Nejd
Source:
Wikipedia (DE), World Statesmen,
Weltgeschichte, Volker Preuß

"Nejd" is Arabian and means "upland".
It is the name for the hilly region which is placed between the Jabal Shammar, the ad-Dahna desert, the Hejaz and the Rub al-Khali desert. Some mountain tops reach altitudes to 1000 meters. There are few oases and sporadic lodes.
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)


![]()


























