
The current flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis was designed by Edrice Lewis and was introduced on 19th of September in 1983 on the occasion of independence. It shows a diagonal, yellow-outlined, black stripe with two white five-pointed stars, a green field at the top left, and a red field at the bottom right. The black represents the African roots of most of the country's inhabitants, yellow stands for the sun and green for the fertility of the land. Red represents the blood shed in the struggle to gain independence. The white stars symbolize the two islands. They also express hope for freedom and peace. The colors are probably not defined, the British Ministry of Defense states the following colors in its regulatory publication "Flags of all Nations": Green = pt 364 c, Red = pt 186 c, Yellow = pt 116 c.
Initially the islands, especially
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), were disputed between France and England/United Kingdom. In the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, United Kingdom was officially awarded
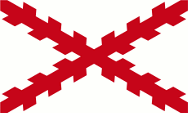
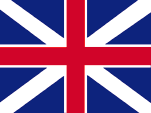
Saint Christopher, so that from that year on the flag of United Kingdom flew unchallenged over the islands, which became administratively part of the British Colony of the Leeward Islands between 1671 and 1816 and then again from 1833. The Leeward Islands were therefore part of the United Kingdom and received their own administration and governor. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the United Kingdom by the use of the Union Jack, called the "Union Flag".
United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner.
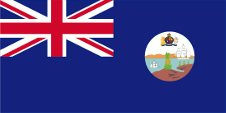
Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for the Leeward Islands. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side. The Leeward Islands received their own badge in 1871. It showed a pineapple on a coast with two ships.
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla had already been administratively united into one colony within the colony of the Leeward Islands in 1882: Colony of
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla. The individual islands were probably already using their own seals, the images of which were combined on a heraldic shield in 1958 when the colony of the Leeward Islands was dissolved and the colony of
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla were allowed to use their own official emblems. This heraldic shield became the colony's badge on a white disc, used on a "Blue Ensign". The escutcheon was divided into three parts and showed the heraldic images of the individual islands: Columbus with a telescope on board of a ship (Saint
Kitts), three virgins at a spring (Nevis) and a native with his boat on a coast (Anguilla).
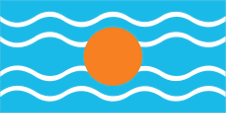
At the same time, the colony was part of the British colony "West Indian Federation" from 1958 to 1962, an attempt to consolidate the administration and also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and colonies. The flag of the "West Indian Federation" was a light blue flag with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many contemporary prints also show this light blue.
On 27th of February in 1967, United Kingdom granted internal self-government and
Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla became an autonomous state associated with United Kingdom. In this context, a new flag was introduced, which ended the tradition of the "Union Flag" and the "Blue Ensigns". This flag featured three vertical stripes of green, yellow and blue, and in the center of the yellow stripe a black palm tree with three branches (Saint
Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla). Flags with the same colors were and are also used in Grenada and St. Vincent. The current flag was introduced on the occasion of independence on 19th of September im 1983.
In 1971, Anguilla was separated and returned to British administration and has been an own colony since 1980.
The flag of Nevis shows the flag of
Saint Kitts/Nevis in the upper corner and in the waving end the outline of the volcano Nevis Peak, which dominates the island. There is also a variant of the flag that features a blue stripe at the base of the volcano.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flags of all Nations,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


since 1967,
Coat of arms of Saint Kitts/Nevis,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

1871–1958,
Leeward Islands,
Badge (Emblem) of the Leeward Islands,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1958–1967,
Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla,
Badge (Emblem) of Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The coat of arms of Saint Kitts and Nevis was introduced on 16th of February in 1967. The shield shows in a blue upper part a lily, the head of a Carib woman and a Tudor rose. This embodies the history of the islands, which have been disputed between Britain and France in the past. In the middle part of the shield, on a silvery background, are two red poinciana flowers, a sailing ship and a red angle (chevron) between them. Supporters are two pelicans. Above the shield is a helmet with golden-black mantling, a black-blue torse and a torch held by three different colored human arms – a symbol of the three races on the islands. The motto in the silvery banner was originally "Unity and Trinity". This was changed to "Country above self" on the occasion of independence, as was the ship, which since 1983 has only one mast instead of two. The badge of the Leeward Islands, which included
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla between 1871 and 1958, showed a pineapple on a coast with two ships.
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla had already been administratively united into one colony within the colony of the Leeward Islands in 1882: Colony of
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla. The individual islands were probably already using their own seals, the images of which were combined on a heraldic shield in 1958 when the colony of the Leeward Islands was dissolved and the colony of
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla were allowed to use their own official emblems. This heraldic shield became the colony's badge on a white disc, used on a "Blue Ensign". The escutcheon was divided into three parts and showed the heraldic images of the individual islands: Columbus with a telescope on board of a ship (Saint
Kitts), three virgins at a spring (Nevis) and a native with his boat on a coast (Anguilla).
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
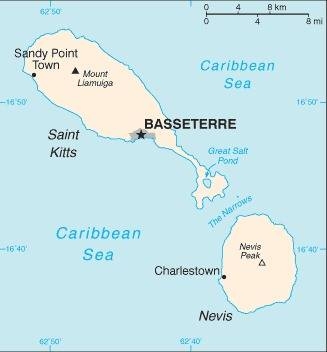
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 101 square miles, thereof Saint Kitts: 65 sq.mi., Nevis: 36 sq.mi.
Inhabitants: 53.000 (2020), thereof 90% Africans, 5,0% Mulattos, 3,0% Asians, 1,0% Europeans (British and Portugese)
Religions: 41% Protestant, 36% Anglican, 12% Roman Catholic
Density of Population: 78 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Basseterre, 14.000 inh. (2021)
official Language: English
other Languages: Creole Dialects
Currency: Eastern Caribbean Dollar (XCD, EC-$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)
Nevis:
Area: 36 sq.mi.
Inhabitants: 11.500
Density of Population: 48 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Charlestown, 1.700 inh.
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

1493 · the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers the islands and names them San Cristóbal (Saint
Christopherus, today shortend to "Saint Kitts") and Santa María de las Nieves, the islands become a Spanish possession but were not colonized
1620 · appropriation of Nevis by England
1623 · settlement of Saint Kitts by Englishmen
1625 · settlement of Saint Kitts by Frenchmen
1627–1666 · Saint Kitts is divided between England and France
1628 · settlement of Nevis by Englishmen from Saint Kitts
1666–1671 · Saint Kitts is French possession
1671–1689 · Saint Kitts is divided between England and France, the British possession becomes affiliated to the Leeward Islands Colony
1689–1690 · Saint Kitts is French possession
1690 · Saint Kitts becomes British possession and affiliated to the Leeward Islands Colony again
1706 · transitional French occupation
1713 · Treaty of Utrecht, United Kingdom earns Saint Kitts officially
1782–1783 · transitional French occupation
1816 · the Leeward Islands Colony becomes dissolved, Saint Kitts becomes fused with Anguilla, Nevis and the Virgin Islands
1833 · re-estbalishment of the Leeward Islands Colony, to 1958 part of the British Leeward Islands Colony
1882 · the British possessions of Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla become fused within the Leeward Islands Colony (Colony of Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla)
1958–1962 · part of the British colony "Federation of the West Indies"
27th of February 1967 · United Kingdom grants interior self administration (autonomy as with
United Kingdom associated state)
1969 · demands for independence on Anguilla
1971 · Anguilla becomes subordinated under the British administration again
1980 · Anguilla becomes separated from Saint Kitts/Nevis and becomes a self-contained colony
19th of September 1983 · United Kingdom grants independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations, but Nevis gets a limited self administration
13th of October 1997 · the parliament of Nevis proclaims the independence of the island, not recognized
10th of August 1998 · a plebiscite on Nevis for independence fails
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN)

As columbus in 1493 discovered the today’s island of Saint Kitts, he named it San Cristóbal (by other sources Isla de San Jorge). The name
Saint Christopher is todays only shortend in use: "Saint Kitts".
As Columbus in 1493 discovered the today’s island of Nevis, he named it Santa María de las Nieves (Saint Maria of Snow), because he thought that the clouds on the volcano Nevis Peak are snow. Through the times became "Nieves" finally to "Nevis".
The Kalinago, the pre-European inhabitants of Saint Kitts, called the island "Liamuiga", which means "fertile land."
Source: Wikipedia (EN)


![]()






















































![]()
