• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 2005,
official,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




since 2005,
Variant in practice,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)





Flag of the SPLM,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1967–1969,
Flag of the provisional government of South Sudan,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: World Statesmen




The flag of South Sudan was adopted on 9th of July in 2005 and features three horizontal stripes of black, red and green with narrow white dividing stripes and a isosceles sky blue triangle with a yellow five-pointed star on the mast. The meaning of the colours of the flag is determined by the South Sudanese government: Black represents the South Sudanese people. Red represents the blood that was shed for the country's independence. Green represents agriculture, natural wealth, the land and the country's progress. White represents peace. Blue represents the water of the Nile, a source of life. Yellow represents unity of the country and hope and determination. The colours of the flag seem to be defined, but nothing on the legal basis could be found, no law and no regulation. The colours are defined, among others, in the HEX color space for RBG: sky blue = #45B4DB, yellow = #FCDE02, red = #DB0A13 and green = #018A2C. This would correspond to the following colors in the Pantone color space: Sky Blue = pt 2985 c, Yellow = Hexachrome Yellow, Red = pt 1788 c and Green = pt 355 c. The design of the flag has so far had little success; internationally, dark blue is usually used instead of sky blue, and in the country the star is sometimes straight and sometimes diagonal. The model for the flag was the flag of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM), which cites the flag of Kenya as the model for its flag. During the first phase of the Civil War (1955–1972), a different flag was popular. This showed five horizontal stripes in red, white, black, white and red in a ratio of 3:1:8:1:3. That was used by the provisional government of South Sudan from 1967 to 1969.
Source: Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen,
Volker Preuß


since 2011,
Coat of arms of South Sudan,
Source: Unknown, vectorisation by Nanin7,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

since 2011,
Seal of South Sudan,
Source: Unknown, vectorisation by Nanin7,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

The coat of arms of South Sudan shows an African fish eagle with its chest covered with a native shield. Behind, crossed, a shovel and a spear. Banners in gold and silver show the name of the country and the country's motto: "Justice, Liberty, Prosperity". The eagle represents strength, resilience, vision and majesty.
Source: Wikipedia (EN)


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
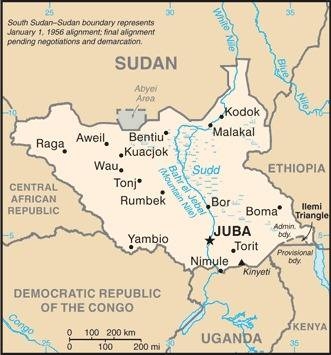
Source: CIA World Factbook
Interactive Map of the Sudan:
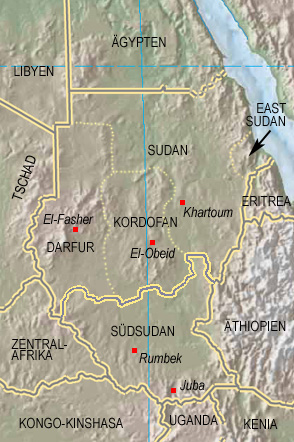
Map: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries,
modyfied by: Volker Preuß

Area: 248.776 square miles
Inhabitants: 11.400.000 (2021), ca. 35-40 % Dinka (Jieng), ca. 15 % Nuer (Naath), furthermore: Shilluk (Chollo), Azande, Bari, Kakwa, Kuku, Murle, Mandari, Didinga, Ndogo, Bviri, Lndi, Anuak, Bongo, Lango, Dungotona, Acholi, Baka, Fertit
Religions: 60.5 % Christian (mostly Catholics and Anglicans), 32.9 % Animist, 6.2 % Muslim
Density of Population: 46 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Juba (Djuba), 500.000 inh. (2017)
official Language: English
other Languages: Arabic, Nilot Dialects, etc.
Currency: 1 South Sudanese Pound (SSP, £SS) = 100 Piastres
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

ca. 1500 – 1700 · Empire of the Fundsh in the southern Sudan, the north becomes dependent from the egypt Mameluks
1863–1875 · Ismail Pasha of Egypt conquers partially the southern Sudan and Darfur (1874)
1875–1881 · the Egyptians try to stop the slave trading
1881–1898 · anti-egyptian-clerical Mahdi revolt under the leadership of Mohammed Achmed, named Mahdi, formation of the Mahdi Empire
1882 · United Kingdom occupys Egypt
1885 · death of the Mahdi, successor is Chalifa Abdullahi
1888–1889 · the Mahdi Empire attacks Ethiopia and conquers the southern Sudan
1898 · Battle of Omdurman, Lord Kitchener destroys the Mahdi Empire
1898 · Battle of Faschoda, Lord Kitchener strikes in southern Sudan invaded Frenchmen
1899 · Sudan is officially administered by Egypt and United Kingdom (Anglo-Egyptian Sudan)
1924 · British attempts to administer separately the north and the south of Sudan
1955 · the christian and animist South Sudan fears a northern and islamic dominance within an independent Sudan and starts the first of all for 17 years enduring civil war
1st of January 1956 · Egypt and United Kingdom grant the Sudan independence, Republic of Sudan
1972 · treaty of Addis-Abeba between the government of Sudan and the South Sudanese Liberation Front, temporary end of the civil war in the south, granting of autonomy for the South Sudan
1983 · South Sudan becomes divided into three separate regions, introduction of the islamic law, the civil war in the south breaks out again
1984 · proclaim of the state of emergency
1992 · offensive against South Sudan
1994 · offensive of South against governmental troops
1996 · isolation of South Sudan
1997 · successful offensive of the south sudanese SPLA (Sudanese People's Liberation Army)
12th of December 1999 · proclaim of the state of emergency, dissolution of the parliament
2005 · Juba – capital of South Sudan – becomes conquered by troops od Sudan, the provisional government moves to Rumbek
2005 · peace agreement, end the fighting, autonomy for South Sudan
2006 · Juba is capital of South Sudan again
2008 · one more fights between Sudan and South Sudan
9th of January in 2011 · beginning of a multi-day referendum for independence in South Sudan
9th of July in 2011 · South Sudan declares its independence
2013–2018 · civil war (mainly between Dinka and Nuer)
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

The Christian and animist people of southern Sudan are engaged in one of Africa's fiercest and most protracted struggles for national independence with the Islamic north. The name "South Sudan" is a factitious term, which binds like a unifying bound around ca. thirty various tribes in the south of Sudan. Every tribe has its own militia and an own government. But the strongest rebel group is the SPLA (Sudanese People's Liberation Army) with perhaps 25 000 men which appears as governmental troops of the South Sudan. The name of Sudan is derived from the Arabian denomination "Bilad es-Sudan". That means "Land of the Black" and describes actually the whole region between Sahara and the African rain forest from western to eastern Africa. In antiquity and in the middle ages the land was called "Nubia", named by the Nubians, an African tribe which lives in the north of Sudan on Nile River.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()














![]()
