mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
- 1561–1795
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

Merchant flag,
Source, by: FOTW, crwflags.com



possible sea flag in the colonies,
Source, by: FOTW, crwflags.com




About the flags of Courland exist very different indications, with probably much speculation, confusion and erroneous descriptions. Fact is that Courland as a former naval power, that has colonized some places in America and Africa, used to have a fleet, and therefore must have been some flags. But which one? Following historical or historicizing images of ships, then occures a red flag with an often black coloured crab. It is also described in the book "Worlds navigation flags" of 1772, which is located in the Latvian Academic Library. The nearby text shows: "the sea crab on the Raspberry red background - the flag of military ships of Duke Jacob". That this really was a pure naval flag, is probably to rule out. It was probably a kind of an sea or merchant flag used overseas in the colonies, in the 17th century. At that time, there were always battles with the Dutch and pirates, trade and the military could not be seen not separated. The colonial activities of Courland were always accompanied by soldiers. At the end of the 17th century the overseas activities of Kurland came to an end. The coat of arms of Courland actually showed a red lion on silver, what would result in a correct implementation of the colors, red over white, on a flag. About such a flag is also reported. As a simple flag with stripes is easy to make and readily available, and it is quite probable as colours of the country or merchant flag. Red and white are also the colors of Poland. The King of Poland was the feudal lord of the dukes of Courland, and the coins of Courland at least temporarily showed the heraldry of Poland. It is also reported about red flags with a black eagle. But this is unlikely. Courland went the same way as Prussia, with a delay of forty years, and submitted itself as the fief of the King of Poland under Polish supremacy. It could have been possible, that Courland get, as well as Prussia, a feudal flag as a symbol of the fief, which represents the symbol of Poland, the eagle, as a colored variant. In Prussia it was the black eagle on white, in the case of Courland it could have been a black eagle on red. However, no fief flag was solemnly handed over to Gotthard Kettler, he was only proclaimed by the Polish envoy to the Duke of Courland and Semigallia. It is also reported about white flags with a black eagle. This is unlikely, too. It will be a confusion with a flag of the Duchy of Prussia.
Source:
irliepaja.lv, crwflags.com


Coat of arms of Courland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

Coat of arms of the Duchy of Courland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

The coat of arms of the duchy of Courland and Semigallia showed a blue and silver quartered shield. In the fields 1 and 4 the symbolism of Courland, a red lion on silver, but crowned, and in the fields 2 and 3 the symbolism of Semigallia, a deer on blue, also with a crown. The depiction of the deer is quite different over the centuries, sometimes it is represented completely, sometimes only the front half, sometimes in natural color, sometimes in silver or even gold.
Source: following pictures - on: hubert-herald.nl

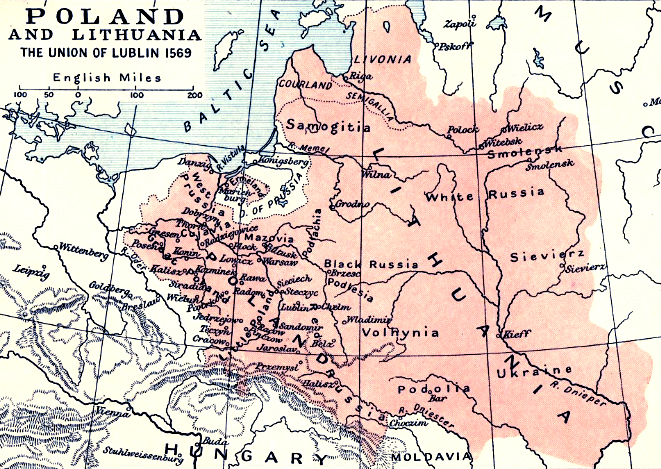
Map Source: Cambridge Modern History Atlas, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
The historical map shows Courland and Semigallia, in the far north, southwestern of Livonia.

Area: ca. 10.530 square miles
Inhabitants: 619.000 (1870)
Density of Population: 59 inh./sq.mi. (1870)
Capital: Mitau (today: Jelgava)
Languages: German, Latvian, Livonian, Latgalian
Currency: Thaler
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

1466 · Second Peace of Thorn, division of the State of the Teutonic Order in 1st) Duchy of Prussia under the King of Poland 2nd) the remaining territory of the Teutonic Order 3rd) Bishopric of Ermland (Warmia)
1525 · the last mayor of the Teutonic Order, Albrecht I. of Brandenburg-Ansbach from the House Hohenzollern, founds the Duchy of Prussia
1558–1583 · Livonian War, a war in and around Livonia between Sweden, Poland-Lithuania, Denmark and Russia
1561 · the chancery of Courland and Livonia subordinates itself under Polish supreme sovereignty, Poland was in this way drawn into the Livonian War, the last Landgrave of the Teutonic Order in Livonia, Gotthard Kettler, founds the Duchy of Courland (actually Courland and Semigallia) as a fief of Poland
1596 · death of Duke Gotthard, division of the duchy into the duchies of Courland and Semigallia between his sons Wilhelm and Friedrich
1616 · Friedrich Kettler reunites both parts of the country
1636 · attempt of colonization on Tobago
1642 · Jakob Kettler becomes Duke of Courland
1651–1658 · the Duchy of Courland operates a trading post on James Island in today's Gambia
1654 · Courland occupies the island of Tobago (renamed in Neukurland), set up of trading posts
1655 · Sweden starts a war against Courland
1658–1660 · Duke Jakob is a prisoner of the Swedish troops
1659 · the Netherlands conquer Neukurland
1668 · an attempt of the reconquest of Neukurland succeeds only partially
1682 · death of Duke Jakob
1686 · Courland sells Neukurland (Tobago) to Great Britain
1700-1703 and 1704-1709 · invasions of Swedish troops during the Northern War
1711 · the duke marries the Russian princess Anna Ivanovna, a niece of Peter the Great, and dies, the rule takes over his uncle Duke Ferdinand Kettler
1726 · the Kingdom of Poland tries to persuade that Courland becomes seized as a done fief and directly attached to Poland, after the death of Duke Ferdinand, who ruled from abroad, but the estates elected the son of the King of Poland, Moritz Count of Saxony, to the duke (as counterpart), who left the country in 1729 because of the politics of Russia
1731 · King Augustus II. of Poland rejects Ferdinand Kettler with Courland
1737 · death of Duke Ferdinand Kettler, the dynasty extincts, Princess Anna Ivanovna, meanwhile Empress of Russia, forces the election of Count Ernst Johann of Biron to the Duke of Courland
1740 · Count Ernst Johann of Biron must go to exile in Siberia
1758 · the estates elect Prince Karl of Saxony as Duke
1763 · Count Ernst Johann of Biron is rehabilitated by the Russian Czarina and returns as Duke of Courland
1769 · Peter, son of Ernst Johann, becomes duke
1795 · Third Polish Division, Courland is annexed by Russia as Governorate of Courland
1914–1918 · First World War: 1915 troops of the German Empire conquer Courland and Semigallia, 1918 troops of the German Empire conquer Lettgallen and Livonia
18th of November in 1918 · Latvia (Courland is until today a part of it) declares its independence, proclamation of the Republic of Latvia
1940–1989 · Latvia belongs to the Soviet Union
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

The name Courland dates back to the Baltic tribe of the Kures, which lived here from the early middle ages to the 15th century, and then merged with Latvians and Germans.
Source:
Wikipedia (D)


![]()









