mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Rwanda
- also: Ruanda
- presidial republic
- own names:
– French: République Rwandaise
– Kinyarwanda: Republika y'u Rwanda
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History

since 2002,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
World Statesmen, Wikipedia (EN)







1898–1916,
German Empire,
Official flag of Colonial Office,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)






1916–1962, Ruanda-Urundi,
Mandate administration,
Flag of Belgium,
ratio = 13:15,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1959–1961,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: World Statesmen






1961–1962,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: World Statesmen






July 1962–31. December 2001,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




The today’s flag of Rwanda was introduced on 1st of January in 2002, together witt a new coat of arms and a new national anthem. This was intended to symbolise a new beginning after the massacres between April and July 1994, which claimed the lives of up to 900.000 Tutsis but also some Hutus. The flag shows three horizontal stripes in the ratio 2:1:1 in blue, yellow and green and a yellow sun in the waving upper corner. The probably not exactly defined colours blue, yellow and green should symbolize the Rwandan peoples of the Hutu, Tutsi and Batwa and their peaceful cohabit. There is also the following interpretation: Light blue stands for fortune and peace, yellow symbolises economic development and green symbolises hope for prosperity. The yellow sun stands for enlightenment. The shades found in practice could be interpreted as: Light Blue = Pantone 299, Yellow = Pantone 116 and Green as Pantone 7483. The side ratio of the flag is given in 2:3 but there are reports about flags in 1:2 too. As in the year 1959 in Rwanda – which was still under Belgian administration – broke out struggles between the Hutu and the kingship of the Tutsi the Hutu created for their own an unofficial flag. This showed three vertical stripes in thr colours red, yellow and green. It was designed after the pattern of the French resp. Belgian tricolour. The Hutu prevailed in the turmoil of the civil war and the republic was proclaimed on 28.01.1961. The Tutsi king Kigéri V was declared deposed and expelled to Burundi. This flag was adopted as the Republic's flag with the reverse colour sequence green-yellow-red, perhaps also to avoid confusion (Guinea used an identical flag). In July 1962, however, they reverted back to red-yellow-green, but a large black "R" was added to the centre of the yellow stripe, presumably again to avoid confusion (Mali uses an identical flag). The "R" first stood for "Rwanda", but also for "referendum" and "revolution". On 1st of July in 1962, Rwanda declared its independence and Belgian administration ended. The red-yellow-green flag with the "R" continued to be used and was retained until 1st of January in 2002. The colors red, yellow and green are even known as the "Panafrican colors": Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african and even american countries in their flags after the independence, stands for the political unity of Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. The introduction of the today's flag implys obviously for Rwanda the farewell from the ideas and ideals of Pan-Africanism, because the Pan-African colours are not in use anymore.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


Coat of arms of Rwanda,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

1962–2002,
Coat of arms of Rwanda,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

The today’s coat of arms of Rwanda (actually a seal) was intoduced – together with a new flag and a new anthem – on the 1st of February in 2002. The coat of arms shows national, african elements, a basket and two shields, even a cogwheel a Sorghum plant, a coffee plant and not finally the sun, which appears in the flag too. The coat of arms shows furthermore in the upper part a golden banner with the name of the state in Kinyarwanda language: "Republika Y'U Rwanda", below a golden banner with the motto of the country: "Ubumwe, Umurimo, Gukunda Igihugu" → "Unity, Work, Patriotism". The both shields symbolize the patriotism, the defense of the national sovereignty but even honesty and justice. The green ring wich surrounds the coat of arms and ends in a knot at the underneath end stands for industrial development by common efforts. The between the 1st of July in 1962 (day of independence) and the 1st of January in 2002 valid coat of arms showed a blazon with hoe, sickle, arrow and bow, as well as the name and the motto of the country in French language. The motto: "Liberté, Cooperation, Progrès" → "Freedom, Cooperation, Progress". A pigeon and a oil twig above and below the shield stood for peace, the tools represented the work and the arms the readiness for defense. In the background two red-yellow-green striped flags.
Source:
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
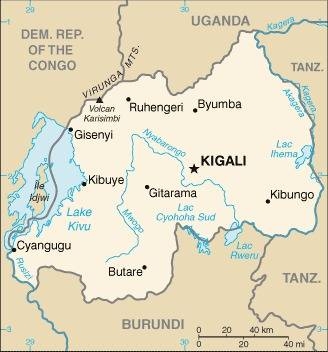
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 10.170 square miles
Inhabitants: 13.300.000 (2021), thereof (estimated) 96% Hutu (Bahutu, Wahutu), 3% Tutsi (Tussi, Watussi, Hima), 1% Twa
Religions: 58% Protestant, 38% Roman Catholic, 2% Muslim, 1% Animist, 1% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 505 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Kigali, 1.745.555 Ew. (2022)
official Languagen: Kinyarwanda, Französisch, Englisch, Swahili
other Languages: Kirundi
Currency: 1 Rwanda-Franc (RWF, FRw) = 100 Centimes
Time Zone: MEZ + 1 h
Source: Wikipedia (D), CIA World Factbook

Antiquity · settlement by Twa tribes
ca. 900 · immigration by farming tribes of the Bantu (Hutu, Kiga), establishment of samaller local kingdoms
ca. 1400 · immigration of the cattle-breeding Tutsi
ca. 1500 · onset of the subjection of the Bantu kingdoms by the Tutsi, establishment of a Tutsi-Kingdom with strict racial segregation in nearly whole Rwanda, parallel evolutions take place except in Rwanda in the whole area between Victoria Lake and Tanganjika Lake (Hima States)
1884 · purchase of private German colonial possessions by Dr. Carl Peters at the coast of East Africa
1885 · foundation of the German East African Colonial Company (DOAG), the German Empire subordinates the private purchased colonial areas in East Africa under its protection
1885 · Congo Treaty, among others arrangement to transfer European wars not to the colonial territories in Africa
1890 · the German-British Helgoland-Zansibar-Treaty subordinates the region of the Kingdom of Rwanda the German Empire
1st of January 1891 · the DOAG transfers the full sovereignty over German East Africa to the German Empire (to German East Africa)
1894 · Count Gustav Adolf von Götzen visits the Kingdom of Rwanda
1898 · protectorate treaty between the Mwami of Rwanda (King of Rwanda) and the German Empire, the Kingdom of Rwanda exists further within the German colonial times and becomes only subordinated under the German supremacy, the kingship becomes supported and strengthend by the Germans
1914–1918 · First World War: August 1914: Great Britain begins to struggle German East Africa in contradiction to the agreements of the Congo Treaty, withdrawal and push aside of the German defence forces, 1916: Belgian troops occupy the Kingdom of Rwanda, 17th of September 1916: the German defence forces leave Tabora, 25th of November 1917: General Lettow-Vorbeck avoids with his troops to Portugese East Africa, September 1918: Lettow-Vorbeck enters with his troops German East Africa again, October 1918: Lettow-Vorbeck avoids with his troops to British Rhodesia, 11th of November 1918: the German Empire surrenders, 25th of November 1918: General Lettow-Vorbeck capitulates under orders of the German government in Abercorn (British Rhodesia)
1920 · Versailles Dictate, the German Empire loses all its colonies, German East Africa becomes separated in two mandates of the League of Nations: 1.) Tanganjika, under the mandate of Great Britain, 2.) Rwanda-Urundi (unification of Rwanda and Burundi) under the mandate of Belgium
1921 · introduction of the mono-cultures of coffee and cotton by Belgium, onset of a potent christian mission
1943/1944 · famine
1946 · dissolution of the League of Nations, Rwanda-Urundi becomes a UN trust territory under Belgian administration
1959 · tensions between Hutu and Tutsi
1960 · elections, victory of the Hutu-Party
January 1961 · dismissal and expulsion of the Mwami (King) of the Tutsi Kigéri V., proclamation of the republic, flee and expulsion of 60.000 Tutsi to Burundi
1st of July 1962 · dissolution of the union with Burundi, proclamation of independence
1963 · from Uganda invades a rebel army consisting of exiled Tutsi in Rwanda, it becomes repulsed
1990 · from Uganda invades once more a rebel army consisting of exiled Tutsi in Rwanda (Front Patriotique Rwandais - FPR), civil war
1991 · new constitution, some concessions to the minority of the Tutsi, the civil war continues
1993 · a UNO Peace-Unit gets stationed
April 1994 · president Habyarimana – a Hutu – dies on the occasion of a plane crash
April 1994–June 1994 · mass homicide of the Hutu against the Tutsi, ca. 900.000 humans become massacred
July 1994 · the Tutsi rebels of the FPR occupy Bujumbura, formation of a provisional government consisting of Hutu and Tutsi
2000 · Paul Kagame, head of the FPR, a Tutsi, becomes president
2003 · new constitution
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


![]()























