mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Tunisian Republic (Tunisia)
- presidial republic
- own name: Al-Dschumhūriyya at-Tūnisiyya
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, state, merchant and naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Naval jack,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag ot the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1793–1827,
Flag of the Ottoman Empire,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1827–1881,
Flag of the Beylik of Tunis,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



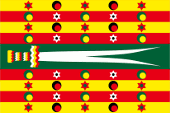
ca.1880–1957,
Flag of the Bey of Tunis,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939




1881–1956, Protecorate,
Flag of Tunisia,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



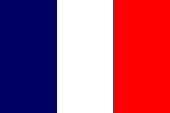
1881–1956, Protecorate,
Flag of France,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






1881–1956, Protecorate,
Merchant flag of Tunisia,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1956–1999,
Flag of Tunisia,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




The flag of Tunisia was created sometime between 1827 and 1831, and was modeled on the flag of the Ottoman Empire (Turkey), under whose sovereignty the area of the Bey of Tunis was at that time. In contrast to the flag of the Ottoman Empire, half-moon and star are are red on the Tunisian flag and lie on a white disc in the center of a red bunting. The reasons for this type of design are obscure and were a mystery even to the Turks at the time. The Turkish Sultan is said to have asked several times what the flag was about, but was never given a reasonable answer. Today it is claimed that the white circular field symbolizes the sun and embodies the unity of the country. The red supposedly represents the blood shed in the fight for freedom. The colour-shade of the red seems to be defined; an indication can be found: Hexadecimal #E70013. A Pantone colour can be derived from this: Pantone 1788 c. The flag was retained during the period as a French protectorate, but it had to be flown on land next to the French tricolor. Only at sea was the Tunisian flag supplemented by the French tricolor in the upper corner. The Bey's flag featured eight red and yellow stripes covered with crescents and stars and a broad green stripe in the middle. Inside is the double-edged sword of Ali, the Prophet Mohammed's cousin and son-in-law. The current presidential flag is also noteworthy, probably for his role as commander in chief of the armed forces. Some images show them with the inscription "Li-l-watan", which means "For the Nation". Photos show a narrow golden border around the disk and around the half-moon and star.
Source:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Volker Preuß


since 1989,
Coat of arms of Tunisia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4

1963–1989,
Coat of arms of Tunisia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4

The today's national coat of arms of Tunisia was introduced on 30th of May in 1963, at that time still as a coloured representation. The shield is – even today – vertically halved and horizontally halved, creating three fields (semi parted per fess and semi parted per pale). The upper field shows a Punic galley, the left, golden field shows a black scale and the right red field shows a black lion with a curved sword. They symbolize justice and order. Directly above the sign is the motto: "Order, Freedom, Justice". Above the shield is a white disc with a red border and the symbols of the flag: red crescent and star. In the official version it shows a golden shield, in practice the fields of the shield are shown in color. In 1989 the coat of arms was changed by changing the colored backgrounds of the three fields to solid gold.
Source: Wikipedia (EN),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
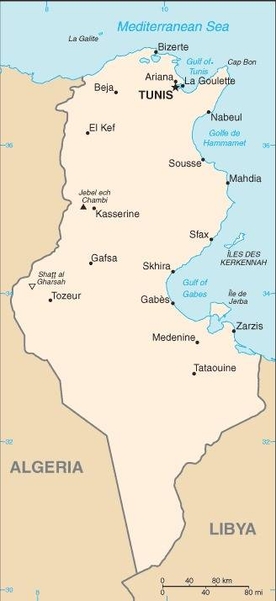
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 63.170 square miles
Inhabitants: 12.400.000 (2023), thereof 67% Tunisian Arabs, 27% Bedouins, 2,5% Algerian Arabs, 1,5% Berber (Amazigh), 2,1% Europeans, 0,8% Jews
Religions: 98% Muslims (mostly Sunnis, some Ibadites), 2% Christians, Jews and Non-religious
Density of Population: 196 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Tunis (Turkish: Tunus), 1.056.247 inh. (2014)
official Language: Arabic
other Languages: Tunisian Arabic, French
Currency: 1 Tunisian Dinar (TND, tD) = 1.000 Millièmes
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source: 1.) Wikipedia (D), 2.) Wikipedia (EN), www.britannica.com

5000 B.C. · settlement by Berbers
1101 B.C. · foundation of Utica by the Phoenicians
814 B.C. · foundation of Carthago by the Phoenicians
ca. 700 B.C. · evolution of the Empire of Carthago
264–146 B.C. · wars against the Roman Empire (Punic Wars)
146 B.C. · demolition of Carthago by the Romans, creation of the Roman province of Africa, Roman settlement
395 · at the partition of the Roman Empire the Province of Africa comes to the West Roman Empire
ab 400 · christianization
439 · conquest by teutonic Vandals and Alans, establishment of the Empire of the Vandals
533 · conquest by the East Roman Empire (Byzantium)
647–698 · conquest by the Arabs with following islamization, the name changes from "Africa" to "Ifriqiya"
800 · Calif Harun ar-Raschid hands Ifriqiya over to Emir Ibrahim ibn Al-Aghlab, establishment of the Aghlabid's dynasty
909 · Ubaid Allah al-Mahdi proclaims hisself to Calif, overthrow of the Aghlabids, establishment of the Fatimid's dynasty
909 · Tunis becomes capital for the first time
ca. 980 · the Fatimide Calif Abu Tamim al-Muizz hands Ifriqiya over to Buluggin ibn Ziri, establishment of the Zirid's dynasty
1057 · overthrow of the Zirids by the Fatimids
1159 · conquest by the Almohad's Sultan Abd al-Mumin
1228 · Abu Zakariya Yahya I. unties hisself from the Almohads, establishment of the Hafsid's dynasty, Ifriqiya becomes an individual state with Tunis as capital
1534 · Admiral Khair ad-Din Barbarossa conquers Tunis for the Ottoman Empire
1535 · Spanish troops conquer Tunis
1574 · Turgut Reis conquers Tunis for the Ottoman Empire, Tunisia becomes a province of the Ottoman Empire
1590 · soldier-revolt, enthrone of a Bey as local sovereign, but Tunisia has to recognize the Ottoman supremacy and has to pay tributes
1612 · enthrone of the Muradit's dynasty under Murad Bey
1705 · overthrow, enthrone of the Husainid's dynasty under Husain I. Ibn Ali Bey
1861 · constitution, constitutional monarchy
1869 · bankrupt of the state
1871 · the Ottoman Empire renounces for its yearly tributes
1880/81 · pillages in French-Algeria by Tunisian Krumirs
April 1881 · invasion of French troops
12th of May 1881 · Bey Muhammad III. al-Husain signs the Bardo-Treaty, Tunisia becomes a French protectorate
April 1938 · anti-French agitations
1939–1945 · Second World War; 1940: Tunisia remained under control of the with the German Empire allied France, 1942: Tunisia becomes besieged by in Algeria debarked US-american troops. November 1942: stop of the advance of the US-Americans by counterstrikes of the German troops until April 1943. 13th of May in 1943: capitulation of the German and Italian troops at Cape Bon near Tunis.
1953 · anti-French agitations
1955 · France grants autonomy to Tunisia
20th of March 1956 · France grants independence to Tunisia
25th of July 1957 · deposition of the Bey, abolition of monarchy, Tunisia becomes a republic
1963 · France withdraws its last troops
1963 · single party system
1963–1969 · transitional socialistic policy
1969 · economic difficulties, agitations
1983 · agitations
1987 · reforms, permission of other parties
2002 · new constitution
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß

The country's name "Tunisia" comes from the name of the city "Tunis". Tunis is a very old city, dating back to 1.000 B.C. existed. The city was once named after the Phoenician goddess "Tanith". Tanith means "serpent lady". However, it was always overshadowed by neighboring Carthage. After the fall of Carthage, the country was called "Africa" as a Roman province, and after the Arab conquest it became "Ifriqiya". From the 13th century, Tunis was the capital of the entire region. This remained the case even after the Ottoman Empire conquered it in 1574. However, as early as 1590 there was a soldier's revolt, which resulted in the enthronement of a Bey as local ruler; the country became the Beylik of Tunis (Turkish: Tunus Beyliği), but had to recognize Ottoman suzerainty and paid tribute. With the growing European influence, "Tunisia" was used as the country's name, if you will, until today, although the country is officially called the "Tunisian Republic". The country's literal name is "Al-Jumhūriyya at-Tūnisiyya" → "Tunisian Republic".
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()





















