mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Cape Colony
- also: Cape Land
- since 1814 British colony
- since 1910 province of South Africa (Cape Province, Kaapprovinsie)
- divided in 1994
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

1814–1875,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source:
Flags of the World






1875–1910,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source:
Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World




The flag of the Cape Colony was a so called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack points out to the connections to United Kingdom. The flag as intended for use by offices and departments and actually only at sea. Residents had furthermore to use the British Union Jack. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other. The Cape Colony became awarded an own coat of arms in the year 1875, which was shown within a wihite disk in the flying end of a "Blue Ensign". As a province of South Africa the country had none own flag anymore until 1994.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World


Coat of arms of the Cape Colony,
Source, by:
Flags of the World

The coat of arms of the Cape Colony showed a red shield with a golden lion which is surrounded by three golden rings. In the head of the shield a silvery field with three blue disks with each one golden lily inside. Shield-supporters were a gnu and a antelope. Above the shield a golden-red torus and on it a female figure with an anchor which is lean against a rock. It symbolizes hope. Below the shield a silvery banner with the motto of the colony: "Spes Bona" → "Good Hope". The motto and also the female figure are hints for the Cape of Good Hope.
Source:
Flags of the World

Map of the country:
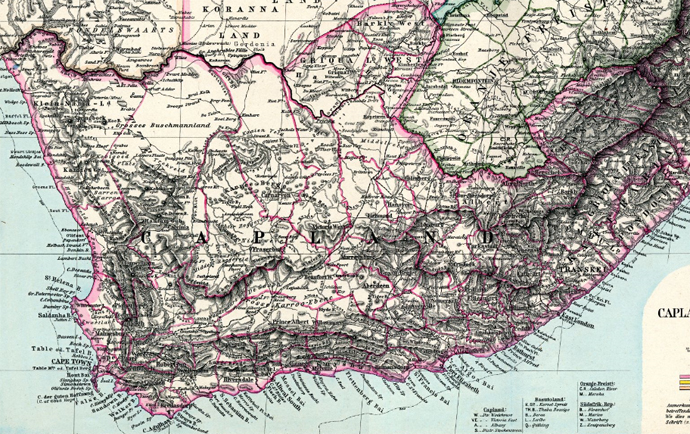
Source:
www.maproom.org
Burenrepubliken und Britische Kapkolonie, heutige Grenzen in Rot:
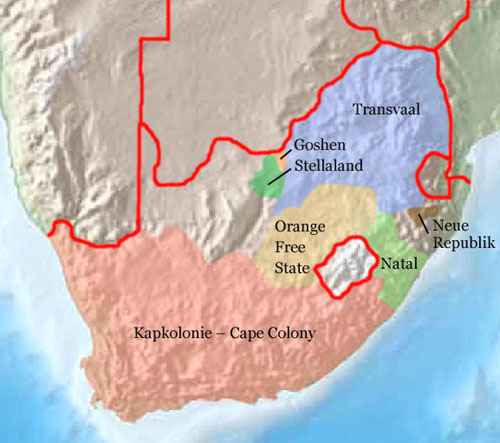
Source:
Freeware, University of Texas Libraries,
modyfied by: Volker Preuß

Area: 278.379 square miles (1982), 220.730 square miles (1891)
Inhabitants: 6.722.000 (1982), 1.526.500 (1891)
Capital: Kapstadt (Cape Town, Kaapstad), 691.000 inh. (1970)
Languages: Afrikaans, English, Bantu Languages
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source, by:
Politische Gliederung der Erde, Brockhaus Konversationslexikon

Antiquity/Middle Ages · in the today’s South Africa live Khoisanide nations (so named Hottentotts or Bushmen)
1488 · the Portugese seafarer Bartolomëu Diaz reaches the Cape of Good Hope
1497 · the Portugese seafarer Vasco da Gama sails around the Cape of Good Hope on the way to India
15th/16th century · immigration of black Bantu nations (Ndebele, Xhosa, Zulu, Sotho, Tswana, Swati, Venda, Tsonga ...)
1602 · the Netherlanders appropriate the land around the Cape of Good Hope (Kapland), settlement of Boers (farmer of Dutch and German descent, self-designation: Afrikaander)
1652 · Jan van Riebeeck founds the smallholding Kapstadt in mission of the Dutch East Indian Company
1806 · United Kingdom occupys Kapland
1814 · United Kingdom annexes Kapland officially, establishment of the British Cape Colony
1833 · abolition of slavery
1836–1885 · the Boers leave Kapland in long treks towards east and northeast and establish various Boer's republics (1838 Natal, 1854 Orange Free State, 1853 Transvaal, 1883 Stellaland, 1883 Goshen, 1884 New Republic ...), the British colonial power haunts the Boers
1866 · annexion of Kaffaria Colony (in the south of the today's South Africa) to the Cape Colony
1885 · annexion of Goshen and Stellaland (in the north of the today's South Africa) to the Cape Colony
1887 · annexion of Zululand (in the east of the today's South Africa) to the Cape Colony
1894 · annexion of Pondoland (in the south of the today's South Africa) to the Cape Colony
1895 · annexion of South Bechuanaland (in the north of the today's South Africa) to the Cape Colony
1910 · United Kingdom joins the colonies Orange Free State, Transvaal, Natal and Cape Province to the South African Union, status of a British dominion for South Africa
27.04.1994 · new constitution for South Africa, division of the Cape Province
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte

The name "Cape Colony" has its roots in the position of the country at the Cape of Good Hope. The Netherlanders called it "Kapland" and as a province of South Africa the country was called "Cape Province".
Source:
Volker Preuß


![]()









