mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Korea (South Korea)
- presidial republic with multi-party-system
- own name: Dachan Minkuk
• Flags
• Historical Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, merchant and naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)






Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the president,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



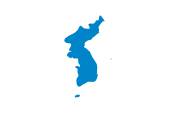
Flag of unification,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: By File:Unification flag of Korea (pre 2006).svg: Variousderivative work: Valentim (File:Unification flag of Korea (pre 2006).svg) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons





1882–1910,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




The flag of South Korea is based on the flag of the former kingdom (to 1910) and shows on a white bunting a red-blue Yin-Yang symbol, which is named in Korean T'aeguk, what means "big polarity" – and in every corner each three, partly complete, partly interrupted black bars, so named trigrams. They are named in Korean Kwae. In this form the flag was for the first time in use in the year 1882 and one year later officially recognized as the symbol of the country. On the 15th of August in 1948 the flag was adoped again for the Republic of Korea (South Korea). On the 25th of January in 1950 it was changed a little bit by modifying of the size of the trigrams and also the size of the T'aeguk. The denomination T'aeguk was transfered in the times for the whole flag. The color white stands for the purity of the thoughts, but is also the traditional colour of the Korean nation. The T'aeguk is known as Yin-Yang symbol in the whole philosophical symbolism of the East. It should symbolize the fusion of the antithesis. Trigrams are cultic characters from the book "I Ging" with philosophical and cosmological relations (sun, moon, earth, heaven or spring, summer, autumn, winter or south, west, north, east). The colours blue and red are supposedly defined hexadecimally, as blue = #CD2E3A and red = #0047A0, from which the Pantone colours blue = pt 294 and red = pt 711 can be derived. The flag of the president is blue and shows a golden hibiscus blossom as well as to the left and on the right two so named "wonder-birds". The naval flag of South Korea is blue with white upper staff quadrant with two crossed black anchora and thereupon the T'aeguk. The "flag of unification" was used, among other things, for the Winter Olympics 2018, when the teams of both Korea appeared under this common flag.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flags of the World,
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen


Coat of arms of South Korea,
Source: Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms shows a red-blue T'aeguk (Yin-Yang Symbol), surrounded by the yellow leafs of the Sharon blossom. It stands for energy and constancy. But by an other interpretation this should be a Hibiscus blossom, which should express hospitality. In the blue field of the banner the name of the state in Hangul fonts.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


since 2005,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1949–2005,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
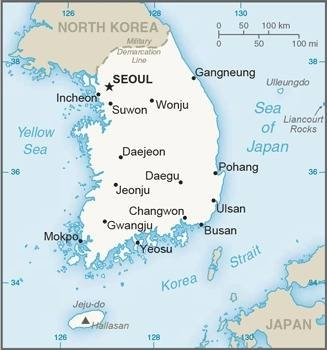
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 38.691 square miles
Inhabitants: 51.800.000 (2020), thereof 99,5 % Koreans, 0,5% Chinese
Religions: 28% Christian, 16% Buddhist, 7% Korean Shamanism, 56% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 1.339 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Seoul (Japanese: Keijo), 9.766.886 inh. (2019)
official Language: Korean
other Languages: English, Chinese
Currency: 1 Won (KRW, W) = 100 Chon
Time Zone: GMT + 9 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

ca. 1100 B.C. · establishment of the Korean state of Choson by Kitcha, the first king of the country and founder of the Kitcha-Dynasty
108 B.C. · subjection of Choson by China
194 B.C. · evolution of three Korean states in the south under the rule of the Chinese Han, in the north arises a Chinese vassal state
1st cent. B.C. · arise of three Korean independent kingdoms (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla)
668 A.D. · the Kingdom of Silla joines all three kingdoms, but Silla disintegrates after 250 years in the empires Silla, Baekje and Madjin, wars between the empires, Madjin asserts oneself, unification of the empires under Madjin, Japan occupies transitionally a coastal stripe in the south (Karak country)
935 · General Wang Gon (Wang Kon) establishes in Madjin the Koryo-Dynasty, the united empire is named Koryo
1229 · Mongolian invasion, rule of the Mongols until 1280
1392 · enthronement of the Yi-Dynasty, which was established by General Yi Sungye (T'aejo), rename of the country in Choson
1592–1598 · Japan attempts to conquer Choson (Korea)
1637 · Choson (Korea) has to recognize the supremacy of the Chinese Mandju emperors, the country begins to insulate itself
1866 · French attempt to conquer the country
1871 · US-American attempt to conquer the country
1876 · Japan coerces the repeal of the isolation, opening of the ports for foreigner mights
1894–1895 · Chinese-Japanese War for the influence in Korea, China succumbs and has recognize the Japanese supremacy in Korea
1904–1905 · Russian-Japanese Krieg for the influence in Korea, Russia succumbs
1910 · Japan annexes Korea as General Government of Chôsen (Choson), end of the Yi-Dynasty
1945 · end of the Second World War, Japan surrenders, Korea becomes partitioned alon the 38th degree of latitude, the north becomes occupied by the Soviet Union, the south by the USA
6th of September 1945 · In the Soviet occupation zone, the "People's Republic of Korea" is founded, whose powers were planned for the whole of Korea; in the South, all its activities are banned on 12.12.1945
8th of February 1946 · the "People's Republic of Korea" project is terminated
10th of May 1948 · election in whole Korea for a employable government, North Korea boycotts the elections
July 1948 · new constitution for Korea
15th of August 1948 · in result of the election gets proclaimed (only in South Korea) the Republic of Korea
9th of November 1948 · in North Korea gets proclaimed the People's Democratic Republic of Korea
25th of June 1950 · North Korean troops invade South Korea, increase into a bigger conflict in which embroil except South Korea even China the USA and respective allies
27th of July 1953 · Armistice of Panmundjom, the country remains separated along the armistice line between North and South Korea
1961 · military coup d'état
1963 · presidental elections
1965 · continuance of diplomatical connections to Japan
1966 · South Korea begins with its engagement in the Vietnam War
1972 · war law, new constitution, presidial dictatorship
1979 · military coup d'état
1985 · small agreements between both Koreas
1988 · new constitution, multy-party-system
1990 · contacts of both Korean governments
1991 · South Korea joines the UNO
1992 · continuance of diplomatical connections to China
1992 · "Treaty of reconciliation, non-aggression, interchange and cooperation" between both Koreas, but increase of the tensions between both states
1997 · discussions about peace between North and South Korea under participation of the USA and China
2000 · diverse humanitarian improvements of the connections between both Koreas
from 2008 · deterioration in relations between the two Koreas
from 2013 · improvement in relations between the two Koreas
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The name "Korea" came to Europe in the middle ages by trading travelers. Either refered this designation to the Korean state of "Koguryo", which exists between the 1st cent. B.C. and the 7th cent. B.C. on the Korean peninsula, or the designation goes back to the dynasty "Koryo", which united the countries in the year 936 und gave the country "Koryo" its name. In the year 1392 the Dynastie "Yi" came to power (until 1910), which renamed the country in the same year in "Choson" (country of the morning freshness). This designation is in use until today by North Korea. South Korea names itself "Dachan Minkuk". But internationally is only in use Korea (North Korea or South Korea).
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()





















