• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Federal States
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Somali States
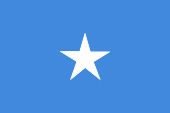
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Italian Somaliland:

1851–1941, Italy,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Das Flaggenbuch




1908–1936,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Das Flaggenbuch




1941–1950, occupied by U.K.,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen






1950–1960,
Flag of Italy,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen






1954–1960,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World





British Somaliland:

1884–1960, Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1884–1960,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations





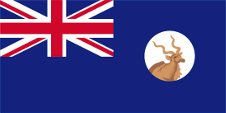
1903–1950,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1903–1950,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1950–1960,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1950–1960,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The today’s flag of Somalia was introduced for Italian Somaliland on 12th of October in 1954 and was tooken over at the independence of the united Somalia on 1st of July in 1960. The flag shows a single-coloured pale blue bunting with a white five-pointed star in the middle. The appearance and colour of the country's flag were last defined in Article 6 of the 2012 Constitution of the Federal Republic of Somalia, and of course in previous constitutions. The colour of the flag is again only defined as "light blue" and the size of the star is repeatedly again not mentioned at all. To explain the meaning of the colours and of the symbolism there are two theories:
• The colours have their roots in the flag of the United Nations, because Italian Somaliland was under its administration between 1949 and 1960. The five-pointed star symbolizes the five regions in which Somali lived about 1954: 1: British Somaliland (today Somaliland), 2. French Somaliland (today Djibouti), 3. Italian Somaliland (today Somalia, Puntland and Galmudug), 4. British East Africa (today Kenya) and 5. Ogaden (part of Ethiopia).
• Blue is the colour of the heaven over the African continent and the white star stands for the African freedom.
When Awale Liban created the flag in 1954, he supposedly referred to the blue of the United Nations (UN) flag. This means that the light blue should officially correspond to the UN blue, which means that Pantone 279 should be used. However, if you look at the upper half of the coat of arms of Italian Somaliland created in 1919, the design and colour of the flag is already quite recognisable. From the territory of the former Somalia separated between 1991 and 2006 at least three states and Somalia itself even momentaryly finished its existence. The both Somalia-States of Puntland and Galmudug (to 2017) use as well the Somali flag. British Somaliland came into being in 1887 after the British had taken power in Egyptian Somaliland in February 1884. Egypt had been conquered by United Kingdom in 1882, but was initially under the administration of British India from Aden. In 1903, British Somaliland received its own administration and thus its own governor. This gave the British administration of the colony the right to use its own so-called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag bunting with a representation of a flag - the British Union Jack - in the upper corner, with a badge in the waving end. For all other purposes, only the British Union Jack was to be used on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", was to be used at sea.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Such a permission had ever been granted for British Somaliland, and so only the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign" without a badge in the waving end, was officially used at sea. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


since 1956,
Coat of arms of Somalia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE), Corel Draw 4

1919–1936
Coat of arms of Italian Somaliland,
Source: Wikipedia (DE),
Angelus, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

1903–1950
Badge of British Somaliland,
Source: Flags of the World

1950–1960
Badge of British Somaliland,
Source: Flags of the World

The today’s coat of arms of Somalia was introduced for Italian Somaliland on 10th of October in 1956 and was tooken over at the independence of the united Somalia on 1st of July in 1960. It shows on a golden bordered shield the motive of the national flag, above that a golden crown as symbol for sovereignty. Shield supporters are two leopards. Below the shield two crossed spears and two crossed palm tree twigs. The spears hold together by a golden banner. In some reproductions however the banner appears in gold. The design goes in part back to the coat of arms of Italian Somaliland, which was been adopted in 1919, because the five-pointed white star on blue background can already be found there, as well as a leopard. The coat of arms of Italian Somaliland was used to 1936, when the country became part of Italian East Africa until 1941. After the Second World War, Italy had to hand over most of its colonial possessions immediately to the victors of the Second World War. Only Italian Somaliland was vacated by the British in 1950 and returned to the Italians, under UN supervision, until the country became independent in 1960. The present coat of arms was introduced as early as 1956. British Somaliland had its own administration from 1903, so its own badge was used here from 1903. It was a white disc with a Kudu Antelope on it. In 1950, a regular coat of arms had been introduced, which now appeared in the badge instead of the antelope. It showed on a white disk a shield and in its head were to see two crossed Somali spears and a Somali shield. The vertically divided shield showed on the one side an arabian dhau (sailing ship with one sail) stylized waves and one anchor, a hint for the establishment of the country by traders and seafarers. In the other side of the shield is to see the "Silvery Minaret", the tower of the main mosque in Hargeisa, and above the shield the head of an Kudu Antelope with the British crown between the horns.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)


Jubaland,
since: 28. Aug. 2013,
Area: 42.584 sq.mi.,
Inhabitants: 1.360.633 (2014)
Capital: Kismayo,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



Koonfur Galbeed,
since: 25. Jun. 2014,
Area: 38.171 sq.mi.,
Inhabitants: 4.387.355 (2022)
Capital: Baidoa,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Hirshabelle,
since: 05. Oct. 2016,
Area: ca. 31.000 sq.mi.,
Inhabitants: 3.771.638 (2020)
Capital: Beledweyne,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Galmudug,
since: 14. Aug. 2012,
Area: 38.750 sq.mi.,
Inhabitants: 3.800.000 (2019)
Capital: Dusmareb,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Location:
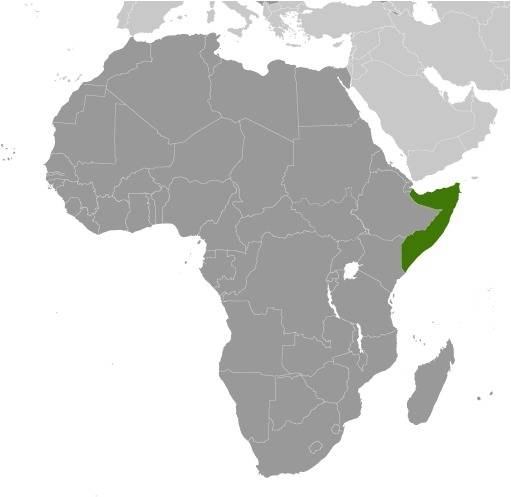
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
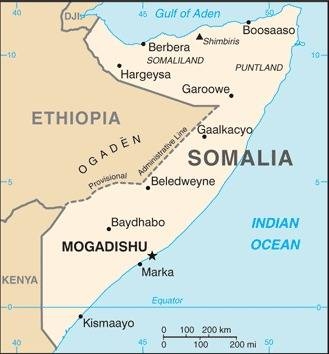
Source: CIA World Factbook
The Horn of Africa, 2012:
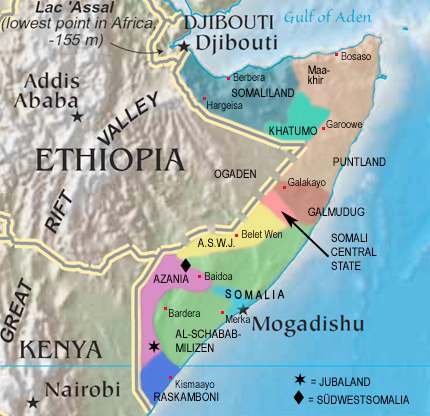
Map: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries,
modyfied by: Volker Preuß
The Horn of Africa, 2023:
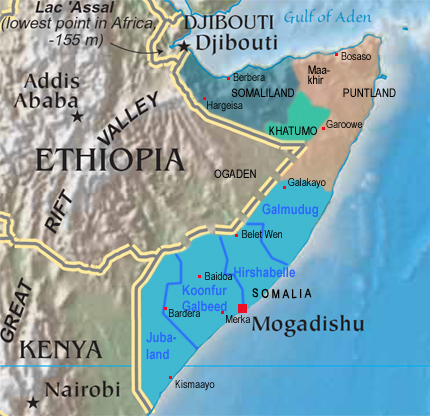
Map: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries,
modyfied by: Volker Preuß

Area: 1991: 246.200 square miles, 2023 (without Somaliland and Puntland): ca. 111.022 square miles
Inhabitants: 1991: 9.250.000, 2023 (without Somaliland and Puntland): ca. 11.191.820 inhabitants, thereof ca. 15% Bantu, 1% Arabs, Indians, Pakistanis
Religions: 99% Muslim
Density of Population: 101 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Mogadischu (Ital.: Mogadiscio), 1.977.000 inh. (2017)
official Languages: Somali, Arabic
other Languages: Italian, English, Zigula, Swahili
Currency: 1 Somali Shilling (SOS, SoSh) = 100 Centesimi (Cent, Senti)
Time Zone: GMT + 3 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

antiquity · trade between the Somali from Punt and Egypt, later also with the Roman Empire
7th century · first contacts with the Islam at the coast
10th century · foundation of Mogadishu, Barawa and Merka by Arabian and Persian merchants, evolution of town-states
15th century · islamization
16th century · conquer of the eastern coast by the Portugese
17th century · the Sultan of Mascat (Oman) conquers the eastern coast and banishes the Portugese
1856 · death of Sultan Seyyid Said of Oman, division of the country (split of the dynasty in two lines) in the Sultanate of Oman and the Sultanate of Zanzibar (with the islands of Zanzibar, Pemba, Lamu, Manda, Patta including the whole African eastern coast between Cape Delgado and Mogadishu)
1885–1890 · the German Empire attempts to acquire colonial property in the area of the Somali east coast through the German East African Society, but conflicts arise with United Kingdom and Italy
French Somaliland: look Djibouti
British Somaliland: look Somaliland
Italian Somaliland:
1889 · Italy occupys the town Obbia at the eastern coast
1892–1893 · Italy leases the possessions of Zanzibar at the eastern coast
1905 · Italy purchases the possessions of Zanzibar at the eastern coast
1908 · formation of the colony of Italian Somaliland
1888, 1894, 1906 · frontier treaties between Italy, United Kingdom, France and Ethiopia, division of the by Somali inhabited territories
1924 · United Kingdom cedes Jubaland to Italy
1926 · Jubaland becomes affiliated to Italian Somaliland
1941 · Second World War, British troops occupy the country
1949 · Italian Somaliland becomes subordinated under Italian administration as an UNO trust territory
1943 · establishment of the "Somali Youth League" (SYL), claims for independence and unification of all Somali countries
1956 · elections, victory of the SYL, formation of a government, Italy grants semi-autonomy
1st of July 1960 · Italy grants independence, unification of the former Italian Somaliland with the former British Somaliland to the Republic of Somalia, President: Adan Abdullah Osman, Premier: A. R. A. Shermake
Somalia:
1964 · war against Ethiopia to gain the by Somali inhabited province of Ogaden
21.10.1969 · coup d’état of General Siyad Mohammed Barre, proclamation of the Democratic Republic of Somalia
1972 · Somali becomes official language, introduction of the Latin writing
1st of July 1976 · introduction of the single-party-system under the Somali Revolutionar Socialistic Party (SRSP)
1977–1982 · war against Ethiopia to gain the by Somali inhabited province of Ogaden, the "West Somali Liberation Front" continues the struggle in Ogaden for the annexion of the province by Somalia
1th of August 1979 · new constitution
1980–1982 · state of emergency, agitations, riots, struggles
1988 · civil war between the government of Barre and the Somali National Movement (SNM)
1989 · all opposing groups join against the government of Barre
1991 · overthrow of the government of Barre, Siyad Mohammed Barre flees to Nigeria, the anti-Barre-alliance breaks, struggles between the opposing groups, especially between the troops of General Ali Mahdi Mohammed and General Aidid, Aidid occupys Mogadishu
24th of May 1991 · the former British Somaliland separates as Republic of Somaliland from Somalia and declares its independence
21st of July 1991 · proclamation of the Republic of Somalia
1992 · US-troops invade Somalia on behalf of the UNO
1993 · the Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM) conquers Jubaland, the area west of the river Juba, international troops invade Somalia on behalf of the UNO
1995 · defeat of the UNO-troops against the Somali, withdrawal of the UNO and its troops from Somalia, death of General Siyad Mohammed Barre in Lagos (Nigeria), the Dir subgroup of the Issa clan proclaims the Republic of Awdal in the far northwest near Djibouti
1996 · death of General Aidid, continuation of the civil war
August 1996 · cease fire
1997 · formation of a government under Ali Mahdi Mohammed
1998–2000 · once more struggles between enemy militias in Southern Somalia and Mogadishu
1998 · the Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM) proclaims the independent state of Jubaland
23rd of July 1998 · separation of the "Autonomous Region of Puntland"
1999 · the Juba Valley Alliance (JVA) conquers Jubaland and proclaims the state of Jubaland, loyal to the central government in Mogadishu
2000 · establishment of an exile government under Abdulkassim Salat Hassan in Arta (Djibouti), recognition by the UNO
2002–2005 · the Rahanweyn clan proclaims and runs the state of South-West Somalia in and around Baidoa
2004 · election of Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed to president in Mogadishu
2005 · attacks of the by Eritrea supported radical-islamic "Union of Islamic Courts", escape of the government of Ahmed to Baidoa
June 2006 · the "Union of Islamic Courts" conquers Mogadishu
14th of August 2006 · separation of the state of Galmudug from Puntland
September 2006 · the "Union of Islamic Courts" conquers Kismayu and Baidoa, Ethiopia sees its territorial integrity endangered and starts air strikes
November/December 2006 · Ethiopian troops and troops of the Somali government start the offensive against the "Union of Islamic Courts"
26th of December 2006 · Ethiopian troops and troops of the Somali government conquer Baidoa
28th of December 2006 · the "Union of Islamic Courts" flees from Mogadishu, marching in of the Somali government
31st of December 2006 · the "Union of Islamic Courts" flees from and withdraws in direction of the frontier to Kenya
2006-2010 · civil war spreads to the capital Mogadishu, mass exodus, countless Somali states are formed, some declare themselves independent, others submit to the central government, Al-Shabab militia emerges from the Islamist group "Union of Islamic Courts"
2009 · Ethiopian troops leave the country, militant Islamists spread throughout the country, emergence of the Islamist group "ASWJ - Al Sunna wal Jamma"
2010-2011 · clashes between the Islamist groups (Al-Shabab, Hizbul Islam), Al-Shabab withdraws from Mogadishu, the state of Raskamboni is founded in Jubaland
2011 · troops of the Republic of Kenya invade southern Somalia to fight al-Shabaab, with the help of African Union troops and from Ethiopia and Kenya, the central government manages to regain a foothold in Mogadishu and stabilise its power, founding of the Republic of Azania in Jubaland
2012 · the Abgal subgroup of the Hawiye clan proclaims the state of Mareeg in the south of Galguduud province, first ideas about the creation of a federal Somalia
25.08.2012 · Proclamation of the Federal Republic of Somalia
2012-2016 · the central government succeeds through negotiations in uniting the many Somali states and separatist movements regionally into four federal states, the main problem remains the Islamist militias, which control about a quarter of the country
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen

The name "Somalia" is derived from its inhabitants. They call themselves "Somali", which supposedly translates as "the hospitable". In Somali, the words "soo mal" mean something like "go and milk", possibly meant as an invitation to drink milk, which perhaps provides the explanation for the assumed hospitality. One can well imagine a foreign traveller landing by ship on the coast, meeting a local who points in the direction of his dwelling and calls out "soo mal", and the guest reinterpreting the gesture as naming the country. On the other hand, in the Cushitic languages of the Horn of Africa, which include Somali, the word "somal" means "dark" or "black", perhaps referring to the very dark skin colour of some Somalis. In Arabic, the word "zamla" means "cattle".
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen, Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()







































![]()
