mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of the Union of Myanmar
- authoritarian presidial republic with multi-party-system
- own name: Pyijchaunsu Myanma Nainngamto
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Secessions
- Kawthoolei – State of Karen
- Arakan
- Mon State
- Shanland
- Mizoram – State of Chin
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 2010,
National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D),
Flags of the World






since 2010 (?),
Flag of the armed forces,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 2010 (?),
Flag of the armed forces,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




since 2010,
Naval war flag,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)



since 2010,
Flag of the air force,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




since 2010,
Flag of the army,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Flag of the President,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World





ca.1700–1886,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN)




1886–1939,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen






1939–1941,
Flag of the government (State flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Wikipedia (EN)




1941–1942,
Flag of British Burma (provisional),
Source, by: World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN)



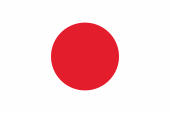
1940–1945,
Burma is occupied by Japan,
Source, by: Flags of the World






1942–1945,
Flag of Japanese Burma / unofficial / Synyethe-Wunthann Party,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1943–1945,
Flag of Japanese Burma / official,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN)




1945–1948,
Flag of the government (State flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Wikipedia (EN)



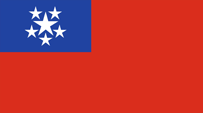
1948–1974,
National flag,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen



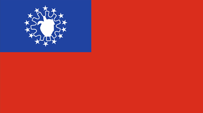
1974–2010,
National flag,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1974–2010,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations



1974–2010,
Naval flag,
ratio = 5:9,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations




The today's flag of Burma was adopted on 21st of October in 2010. It shows three horizontal stripes in yellow, green and red and in the middle a big five-pointed white star. In this way they return to the design of the years of the Second World War under japanese occupation, but there arises the white star of the "Freedom League". The "Freedom League" was the armed anti-japanese resitance. The flag of the from China dependent Kingdom of Burma was initialy single colour white, with the depiction of a peacock in the middle. It was in use until the British annexation in the year 1886. In the year 1939 was introduced for the in 1937 from British-India separated Burma a British Blue Ensign. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" => civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment => the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
Burma, since 1937 with his own government, choiced as badge the peacock again. In 1942 Burma was occupyed by Japanese troops. Since 1942 the domestically power lay with the Synyethe-Wunthann party and its flag was used, in fact until 1945. In 1943 Burma gets independent as Japanese satellite state. The flag of this state showed three horizontal stripes in yellow, green and red, with the peacock on a white disk in the middle. In 1945 Burma was occupyed by British squads, re-incorporated the British colonial empire, and the Blue Ensign was introduced again. On 4th of January in 1948 Burma gets independent once more. The in this context introduced flag was red with a blue upper canton, in it a white five-jagged star, surrounded by five smaller stars. Her origin has this flag in the flag of the anti-japanese "freedom league", a red flag with a white star in the upper canton. The five smaller stars in the new flag stood for the five largest ethnic groups in the land. In context with the introduction of a new constitution was introduced a new flag on 3rd of January in 1974, too. It corresponds to the previous pattern, however it shows instead of the stars a sprocket with a rice plant, circular surrounded by fourteen stars. The sprocket stands for the industry, the rice plant for the agriculture, and the fourteen stars represent the seven states and seven provinces of the land. The peacock is only still in use in the flag of the president. All other flags of Burma were orientated in their styling in the British ensign system, until the introduction of the flag of 2010. The colors given for the flags today are: yellow = pt 116, green = pt 361, red = pt 1788 and white.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Volker Preuß


1948-1974,
Coat of arms of Burma,
Source:
Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (EN),
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen

1974-2010,
Coat of arms of Burma,
Source:
Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (EN),
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen

since 2010,
Coat of arms of Burma (Myanmar),
Source:
Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (EN),
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen

The In 1948 introduced coat of arms of Burma showed a seal in the middle, with a map of the country. Around the map was placed a golded lined red ring with the motto: "The unity leads to happiness and prosperity". Below was placed a pink banner with the name of the country. The seal was guarded by three blue lions. They stand for courage, strength and cleanliness, the number three is a lucky number. The elements of the crest were bond with lush golden belts, blankets and ornaments. In 1974 the constitution was amended. The country was now called "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma". Also, the coat of arms was modified. One of the lions was removed and bevame replaced with the white star of the Freedom League. The central seal was now surrounded with a golden wreath. In the middle of it appeared a silver gear on blue background, a red silhouette of the country was laid over it. In 2010 the constitution was amended again. The country is now called "Republic of the Union of Myanmar". The coat of arms became also changed again. It now appears completely in gold on a red background. The main seal is completely gone, a map / silhouette of the country appears in central position, surrounded by a wrath of two stylized branches.
Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (D)


Aircraft roundel (marking),
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Fin Flash,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
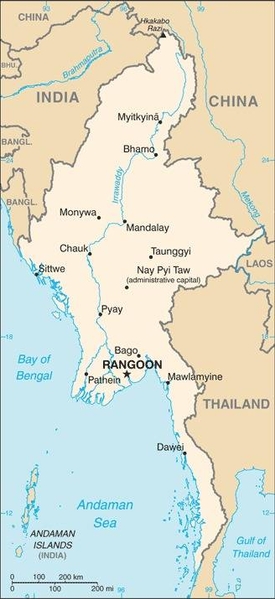
Map of the country:
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 261.227 square miles
Inhabitants: 53.370.600 (2017), thereof 70% Burmese, 8% Shan, 6% Karen (mostly Christian), 2% Mon, 2% Chin
Religions: 88% Buddhist, 5% Protestant, 4% Muslim, 1% Roman Catholic
Density of Population: 204 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Nay Pyi Taw (Naypyidaw), 1.160.242 inh. (2014)
former Capital and bigest city: Rangoon (Yangon), 5.210.000 inh.
official Language: Burmese
other Languages: Shan, Karen, Chin, ...
Currency: 1 Kyat (MMK, K) = 100 Pyas
Time Zone: GMT + 6,5 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

840–1287 · State of Pagan
1287 · Mongol conquest
1364 · Establishing of the Kingdom of Awa, First Empire
1559 · Awa desintegrates into some smaller states
1752 · re-establishing of the Kingdom of Awa, Second Empire
1769 · Awa becomes tributary of the Chinese Empire
1784 · Arakan annexed by Awa
1824–1826 · war against United Kingdom, Rangoon, Arakan, Tenasserim, Manipur, Assam and the coast are annexed to British India
1852–1853 · war against United Kingdom, Pegu is annexed to British India
1862 · Arakan, Tenasserim and Pegu become united administratively as Lower Burma within British India
1885–1886 · war against United Kingdom, the Kingdom of Awa becomes annexed to British India as Upper Burma, and after one month united with Lower Burma to "Burma"
1st of April in 1937 · Burma gets separated from British-India, internal self government
1942–1945 · occupation by Japan in Second World War
1943–1945 · Shanland is annexed by Thailand
1943–1945 · Republik of Burma under Japanese supremacy
4th of January 1948 · United Kingdom grants independence
2nd of March 1962 · Ne Win revolt
4th of January in 1974 · new constitution, rename in Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
1988 · military coup d’état, rename in Union of Burma
1989 · rename in Union of Myanmar
1990 · riots
2005–2007 · move of the capital to Naypyidaw
2007 · riots
2007 · governmental program "to destroy the Christian religion in Myanmar"
21st of October in 2010 · new constitution, rename in Republic of the Union of Myanmar
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The name "Burma"derives from the people of the Burmese, who call themselves "Bamar". The same people also called themselves "Myanma", meaning "the strong". The Burmese represent 70% of the population. In Germany is often used the name "Birma", what is a germanization of the english pronunciation of the word "Burma". However, in Switzerland, Austria and also in the former GDR (Eastern Germany), "Burma" is used. The renaming of the country to "Myanmar" occured in 1989 unilaterally by the military government. The UN has accepted the change, while the USA and Australia ignore it officially. Burma's opposition supports also the maintenance of "Burma".
Source: Wikipedia (D)


![]()





































































