mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- 1798–1918 Principality of Lippe
- from 1918 Free State of Lippe, country of the German Empire
- 1947 incorporated to North Rhine – Westfalia
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Cockade
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

ca. 1820–1904,
Flag of the country (colors),
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1856–1876,
State flag,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1876–1904,
State flag,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1904–1918,
State flag and flag of the country (colors),
Source, by:
World Statesmen




to 1918,
Flag of the Prince,
Source, by:
tmealf.com




1918–1934, Free State of Lippe,
State flag and flag of the country (colors),
Source, by:
www.gonschior.de




since 1973,
Flag of the District of Lippe,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)





The country's flag showed initially two stripes in red and gold, the colors of the house of the Princes of Lippe out of the family line of Lippe-Detmold. In the 19th Century, the country was very often governed by regents, who belong to other branches of the house of Lippe (Schaumburg-Lippe, Lippe-Biesterfeld), or even other and foreign houses (Anhalt-Bernburg). When the throne became vacant, arised a inheritance-dispute between the lines of the house of Lippe, which the Supreme Court in Leipzig in the year 1897 decided in favor of Count Ernst of Lippe-Biesterfeld. When his son Leopold in 1904 ascended the throne, the sequence of the colors on the flag has been reversed, because the line of Lippe-Detmold line was no longer present, and the line of Lippe-Biesterfeld took over. Therefore, the flag showed since 1904 two stripes in gold and red, the colors of the house of the Princes of Lippe from the family line of Lippe-Biesterfeld.
Another incident for the flag was the seizure of power by the National Socialists in the German Empire in 1933. All official non-swastika flags, that refered to federalism, regional references or the old German Empire were abolished between 1933 and 1935. For the National Socialists, the federal structure of the German Empire, its historically grown countries, was considered as outdated, as relics of a past to be overcome. In this sense, several laws were enacted, on 31st of March in 1933 the 'Provisional Law for the phasing of the countries with the Empire', on 7th of April 1933 the 'Second Law for the phasing of the countries with the Empire' and finally, on 30th January in 1934 the 'Law on the rebuilding of the empire'. Thus, the federal structure of the German Empire was replaced by the gau-structure of the NSDAP, the countries became meaningless. From now on, offices and authorities had to use the swastika flag as official flag, until September 15th in 1935, when by the flag-law was legislated a new created official flag for all the offices and authorities of the empire. The prime ministers of the countries, which latest in 1933 all came from the NSDAP – now mostly called Reichsstatthalter (maybe translated as 'governor') – however remained in office until 1945. The corresponding country colours continued, with restrictions, but definitly not in the form of flags. They were used, for example, occasionally on uniforms of the SA or in some ranks of the Hitler Youth in the breast cord.
After the war, the administration within the German Empire was rebuilt, but locally, following the structure of the countries. These have been partly old countries, and some new countries were created. Sometimes they bethought the old country colours and reactivated them – or they created new ones – for limited sovereign duties, which were under the control of the Allies. With the founding of the FRG and the GDR, an internal country-structure was finalised for both entities and corresponding official flags were introduced for these countries.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuß,
Jürgen Kaltschmitt,
Uniform-Fibel


Coat of arms of the Lordship of Lippe,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

Coat of arms of the County of Schwalenberg,
Source:
Heraldique Europeenne

Coat of arms of the County of Sternberg,
Source:
Heraldique Europeenne

1528–1687,
Coat of arms of the County of Lippe,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1687–1798,
Coat of arms of the County of Lippe,
Source: Wikipedia (D)
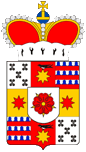
1798–1918,
Middle coat of arms of the Principality of Lippe,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1720–1918,
Lesser coat of arms of the Principality of Lippe,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1918–1947,
Coat of arms of the Free State of Lippe,
Source: Deutsche Ortswappen

since 1947,
Coat of arms of North Rhine-Westfalia,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

since 1973,
Coat of arms of the District of Lippe,
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

The lesser coat of arms of the lordhip, of the county, of the Principality and of the Free State of Lippe showed always a red rose, from the late Middle Ages with golden petals, on a silvery shield. It is called the "Lippe Rose". In 1528, on the occasion of the elevation to the title of a Count, the coat of arms with the rose was added in quarter style, by the heraldry of the County of Schwalenberg (golden star with a swallow on red), which had been acquired in 1365 for the most parts. In 1687 the shield was added by the heraldry of the places Vianen (black columns on silver) and Ameide (six-fold divided between iron hats and red), and placed on the existing sutcheon in a quarterrd heart shield, because the lordship of Vianen and Ameide had been acquired in 1687 by the Counts of Lippe. In 1725 the lordhip was sold, but maintained in the heraldry. In practice, the heraldry of Vianen Ameide was often shown incorrectly, Vianen by red columns on gold or red mill iron crosses on gold, Ameide as a fourfold in iron hats divided field. The coat of arms was newly arranged in 1789, on the occasion of the elevation to the rank of a Prince; with nine fields, added by the heraldry of the County of Sternberg (red Star on gold), which was acquired in 1424. Over field 5 (in the middle of the shield) was placed a silvery heart shield with the "Lippe Rose". In practice, for simplicity, was nearly exclusively used the lesser coat of arms with the "Lippe Rose", and it was even adopted in 1918 by the Free State of Lippe, but the prince's crown was removed and displaced by the "people's crown" . The "Lippe Rose" appeared since 1947, after annex of the country, in the coat of arms of the country North Rhine-Westphalia.
Source, by: Wikipedia (D),
Heraldique Europeenne,
Volker Preuß

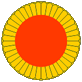
to 1919,
Cockade of Lippe-Detmold

Read here:
Informations, history and facts about the theme "Cockades".
Cockade

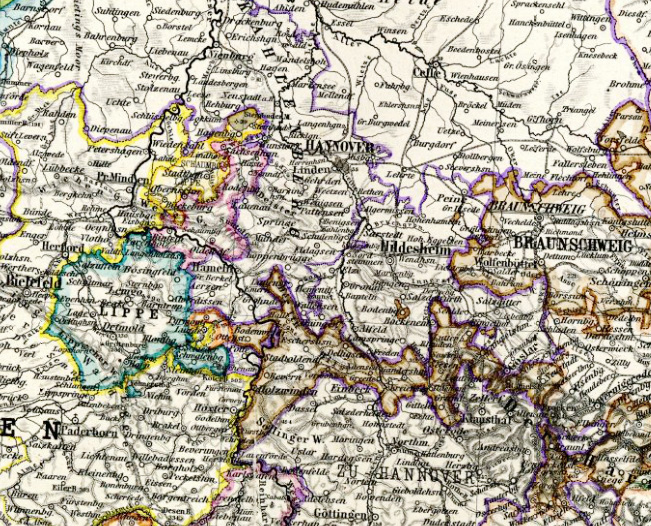
Source: Stielers Hand-Atlas, Justus Perthes, 1891
The map shows the Principality of Lippe ca. 1865 within a blue border.

Area: 469 km²
Inhabitants: 175.500 (1933)
Density of Population: 374 inh./sq.mi. (1933)
Capital: Detmold
Currency to 1847: 1 Taler = 36 Groschen = 216 Pfennige
Currency 1847–1875: 1 Taler = 30 Groschen = 360 Pfennige
Currency 1875–1924: 1 Mark = 100 Pfennig
Currency 1924–1948: 1 Reichsmark (RM) = 100 Reichspfennig (Rpf.)
Source: Wikipedia (D),
HGISG Geoinform,
Der Michel

1123 · a nobleman named Bernhard of Lippe is first mentioned in a document
1365 · the Lords of Lippe inherit the County of Schwalenberg
1424 · the Lords of Lippe inherit the County of Sternberg
1528 · Simon V. of Lippe is levied to an Imperial Count, the Lordship of Lippe becomes to the County of Lippe
1546–1547 · defeat in the Smalcald War, Lippe becomes a directly fiefdom of the empire
1613 · death of Simon VI.
1618–1648 · Thirty Years War, 40% of the people become murdered or die
1621 · inheritances between the three sons of Simon VI., arise of the the family-lines of Lippe-Brake, Lippe-Alverdissen, Lippe-Detmold
1627 · Lippe-Biesterfeld splits from Lippe-Detmold
1644 · the line of Lippe-Alverdissen assumes the County of Schaumburg (Schaumburg-Lippe)
1681 · death of Philipp of Lippe-Alverdissen, inheritance between the two sons, Friedrich Christian gets Schaumburg-Lippe, Philipp Ernst gets the line of Lippe-Alverdissen
1709 · the line of Lippe-Brake extincts
1749 · the line of Lippe-Alverdissen extincts
1762 · Lippe-Weissenfeld splits from Lippe-Detmold
1789 · Leopold I. of Lippe is levied to a Prince, the County of Lippe becomes Principality of Lippe
1792, 1796, 1800 and 1805 · invasions of French revolutionary troops under Napoleon in the German Empire, the German Empire subjectes and becomes territorially transformed
1803 · German Mediatisation (Reichsdeputationshauptschluss), transformation of the territorial partition of the German Empire, ecclesiastical possessions become confiscated, old princely territories and free cities become confiscated or dissolved or annexed to old or new principalities, the number of sovereign authorities and territorial entities of the empire is thus reduced from 300 to 60
12th of July in 1806 · Napoleon forces the creation of the Rhine Confederation, an alliance of sixteen southern and southwestern German states under French protectorate
1st of August 1806 · the states of the Rhine Confederation declare themselves sovereign and resign from the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation
6th of August in 1806 · Emperor Franz II. lays down the crown of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the empire ends
18th of April in 1807 · Lippe-Detmold joins the Rhine Confederation
October 1813 · Napoleon's defeat at Leipzig, the Rhine Confederation begins to fall apart, Napoleon and his troops withdraw behind the Rhine River
1814–1815 · Congress of Vienna, reconstruction of Europe after the era of Napoleon, the ownership and the administrative partitions in the former German Empire become restored, but not the sovereignty of the ecclesiastical countries, their possessions become transferred to old or new principalities, the 39 remaining German states – in this way Lippe-Detmold too – become organized in a loose association, the German Confederation
1866 · German war (civil war), Prussia and its allies against Austria and his allies, Prussia wins, the Principality of Lippe is on the side of Prussia, joining to the North German Confederation
1871 · joining of the Principality of Lippe to the German Empire
1897 · the Supreme Court in Leipzig decides in the case of the succession in favor of Count Ernst of Lippe-Biesterfeld
1918 · fall of the monarchy, establishing the Free State of Lippe
1920 · first republican constitution
1934 · the territorial structure of the states of the German Empire becomes replaced by the districts of the NSDAP, the countries become meaningless
1945 · occupation by British and American troops
21st of January in 1947 · dissolution of the Free State of Lippe, Lippe becomes attached to the Country of North Rhine-Westphalia
1973 · Bielefeld-law: establishing of a District of Lippe by melting of the former Districts of Lemgo and Detmold
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuß

The name of the country has its roots in the Lords of Lippe. The Lippe is a 85 miles long affluent of the River Rhine in Westphalia. The Romans called the river Lippia, what means "the runny".
Source: Volker Preuß







![]()


































