mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- presidial republic
- own name: République démocratique du Congo
- former names:
1885–1908 Congo Free State
1908–1960 Belgian Congo
1960–1966 Congo-Léopoldville
1966–1971 Congo-Kinshasa
1971–1997 Zaire
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• regional Flags
– Katanga
– Southern Kasai
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

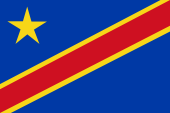
since 2006,
National flag,
ratio = 3:4,
Source: Wikipedia (D)






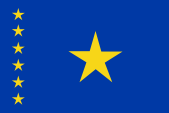
1877–1908,
National flag of the Congo Free State




1908–1960,
National flag of Belgian Congo



1908–ca.1950(?),
Standard of the Governor General of Belgian Congo,
Source, by: Bulgaria Bildband Fahnenbilder




ca.1950(?)–1960,
Standard of the Governor General of Belgian Congo,
Source, by: Flags of the World



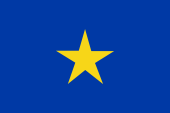
1960–1963,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)






1963–1966,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)



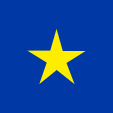
1966–1971,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




1971–1997,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




1997–2003,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)





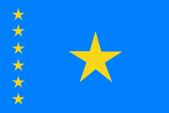
2003–2006,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




The today's flag of Congo-Kinshasa was introduced on 18th of February in 2006. A similar flag was already in use between 1963 and 1971. The flag consists of a pale blue bunting with a yellow five-pointed star in the upper staff quadrant and a red, yellow bordered diagonal stripe. The colour values given for the flag are: Light blue = Pantone 299, red = Pantone 186, yellow = Pantone 107. The colour blue should stand for peace among the peoples of the Congo, the red for the blood of the fighters who died in the fight for freedom, the gold stands for prosperity. The star symbolizes the unity of the country and the diagonal stripe symbolize the future. The flag of the Congo Free State - which was already and ostensibly created in the year 1877 by Henry Morton Stanley - was blue with a big yellow star in the middle. It was also maintained during the Belgian colonial time. In context with the achievement of the independence on the 30th of June 1960 were added on the hitherto flag six little yellow stars for the provinces near the flagstaff. In this way the flag showed at that point of time a blue bunting with a big yellow five-pointed star in the middle and six smaller yellow five-pointed stars on the flagstaff. The big yellow star stood for the nation and the small stars for the then six provinces. The colour blue symbolized at that point in time the heaven above the country and the yellow the natural resources of the country. This flag was in use until the 30th of June in 1963, but was re-introduced after the Zaire era (1971–1997) and was used until 2003 and was used again in light blue until 2006. Because of that, that two provinces leaved the state of Congo between the years 1960 and 1963, they had really to remove in this time two stars from the hitherto valid flag. To prevent such tendencies and even to push aside the role of the province in the background was created a complete new flag. This new flag was adoped on the 1st of July in 1963 and in 1966 changed a little bit. The bunting showed a dark blue again and only one single yellow star in the upper staff quadrant and a red, yellow bordered diagonal stripe. This flag became the template for the flag, which was introduced in light blue in 2006. First, however, on 24th of November in 1971, a green flag with a golden disc stood in its place, thereupon a brown arm which holds a brown torch with a red flame. It was adoped in context with the rename of the country in "Zaire". Arm and torch symbolized the revolutionar spirit of the nation, the red flame honors the martyrs of the struggle for independence. Green is the symbol of the hope for future. That flag based on thr party flag of the MPR (Mouvement Populaire de la Revolution), but also contained the Panafrican Colours red, yellow and green (look → Ethiopia).
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (EN),
Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen


1885–1908,
Coat of arms of Kongo Free State,
Source: Wikipedia (FR)

1908–1960,
Coat of arms of Belgian Congo,
Source: Lesser coat of arms of Belgium.svg: Katepanomegas und Sodacan gemeinsam; Schild Kongo Freistaat.svg: MS05L.MS05L at de.wikipedia [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons

1960–1963,
Coat of arms of Kongo-Léopoldville,
Source: MS05L [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons

1963–1971,
Coat of arms of Congo-Kinshasa,
Source: Coats_of_arms_of_Zaire_1971-1997.svg: Tadpole9derivative work: MS05L [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons

1971–1997,
Coat of arms of Zaire,
Source: Corel Draw 4

1997–1999,
Coat of arms of Congo-Kinshasa,
Source: Coats_of_arms_of_Zaire_1971-1997.svg: Tadpole9derivative work: MS05L [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons

1999–2003,
Coat of arms of Congo-Kinshasa,
Source: via Wikimedia Commons

2003–2006,
Coat of arms of Congo-Kinshasa,
Source: via Wikimedia Commons

since 2006,
Coat of arms of Congo-Kinshasa,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

On 18th of February 2006 the today's coat of arms was introduced. It shows again the until 1997 used leopard-head escorted by an elephant-tusk and a spear. On a pedestal a banner with the motto of the country: "Justice, Paix, Travail" → "Justice, Peace, Work". The coat of arms of Zaire showed a head of a leopard, which was surrounded by a palm-twig and an elephant's tusk. In the foreground crossed an arrow and a spear. Below a banner with the motto of the country: "Justice, Paix, Travail" → "Justice, Peace, Work".
Source:
Wikipedia (D)


since 1997,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1992–1997,
Aircraft Roundel,
Zaire,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
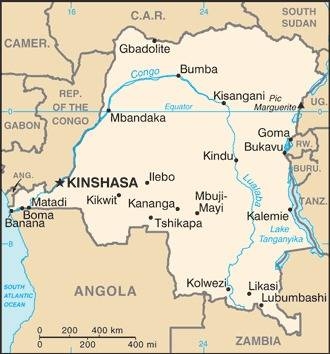
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 905.350 square miles
Inhabitants: 5.546.307 (2022), thereof 18% Luba (Bantu), 16% Kongo (Bantu), 13% Mongo (Bantu), 10% Ruanda (Bantu), Azande, Bangi, Ngale, Nilots, Pygmies and Hima
Religions: 50% Roman Catholic, 20% Protestant, 10% other Christian, 10% Muslim, 10% Animist
Density of Population: 102 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Kinshasa (to 1966 Léopoldville), 14.970.000 inh. (2021)
official Language: French
other Languages: Tshiluba, Congo, Lingala, Suaheli
Currency: 1 Congolese Franc (CDF, FC) = 100 Centimes
Time Zone: GMT +1 h to GMT +2 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

15th century to 19th century · Congo Empire in the west, Luba Empire and Lunda Empire in the middle of the today's Congo-Kinshasa
18th century to 19th century · Kuba Empire in the middle of the today's Congo Kinshasa
19th century · Kassongo in the east of the today's Congo-Kinshasa, the Arabic influence expands from the east to the Congo River
1876 · the explorer Henry Morton Stanley begins to purchase large properties in the Congo Basin for king Leopold II. of Belgium
1884–1885 · Berlin Congo Conference, recognition of the possessions of Leopold II. as Congo Freestate by the european powers
1891 · Katanga comes to the Congo Freestate
1908 · dissolution of the Congo Freestate, establishment of a direct Belgian colonial administration, rename in Belgian Congo
1920 · the territories Ruanda and Urundi, components of the former German East Africa, get incorporated to the Colony of Belgian Congo in accordance with the Versailles Dictate as a mandate of the League of Nations
30th of June 1960 · independence for the former Belgian Congo as Republic of Congo, few times later army revolt, the provinces Katanga and Kasai declare itself for independent, civil war to 1965
1961 · renamed in Federal Republic of Congo
1962 · the State of Kasai surrenders
1963 · UN troops invade the State of Katanga
1964 · withdrawal of the UN troops, renamed in Democratic Republic of Congo
25th of November 1965 · General Joseph-Désiré Mobutu coups hisself to the power
1966 · rename of many towns with European names (e.g. Stanleyville in Kisangani)
1967 · foundation of the unity's party "Revolutionar People's Movement" (MPR), new constitution, single-party-system
23rd of October 1971 · rename of the country from Congo in Republic of Zaire, rename of Katanga in Shaba
1977 · Katangian rebels invade from Angola to Shaba (Katanga)
1978 · Katangian rebels invade again from Angola to Shaba (Katanga)
1991 · social riots, introduction of the multi-party-system
1993 · Governor Gabriel Kyungu Wa Kumwanza prompts officially the rename of the province in Katanga and declares it for autonomous
1996 · struggles between Hutu and Tutsi, begin of the civil war against Mobutu
1997 · fall of the Joseph-Désiré Mobutu by armed forces and tribal militias, Mobutu goes in exile to France and dies, new Chief of the State becomes Laurent Désiré Kabila, rename of the country from Zaire to Congo (Democratic Republic of), the Tutsi militias struggle against Kabila now
30th of June 1998 · introduction of the Congolese Franc
2nd of August 1998 · Tutsi militias and troops from Rwanda and Uganda start an until today maintaining open war against the central government
16th of January 2001 · president Laurent Desiré Kabila gets assassinated, successor is his son Joseph Kabila
2015 · Katanga is dissolved by decision of the President of Congo-Kinshasa and divided into four individual Provinces (Haut-Katanga, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, Tanganyika) and implemented by law on the new regulation of the provinces
2019 · Joseph Kabila is voted out
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Länder der Erde

"Cong" means in the language of the Bantu "Mountain". Obviously the name "Mountain" was given by the indigenous people for the whole river, indeed, its source is in the Mountains. The both Congos get popularly and officially differentiated by the supplement "Republic" or "Democratic Republic". This is not functional, because such designation could change very quickly and moreover they do not reflect the state-legal realities. The adjustment to differentiate the both Congos by attach of the name of the capital it wide spreaded, far purposefuller and is proven in the past.
The designation "Zaire" was not a word-creation of Mobutu, but Mobutu remembers an old – from the Bantu in the 15th century used – designation for the upper part of the Congo River. He wanted to characterize the name of the country more authentical and more original. "Zaire" derives from the Bantu word "n'zadi", what means "big water".
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()















































