mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Estonia
- presidial republic
- own name: Eesti Vabariik
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• regional Flags
– Livonia
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Maps of the History of the Balticum

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flaggen-Atlas Erde






Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




Flag of the border patrol,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the president,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the minister of defense,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the commander in chief,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World




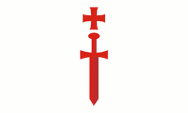
1230–1237,
flag of the Order of the Sword Brothers (Livonian Order)



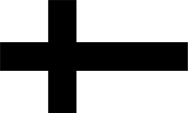
1237–1561,
Flag of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights)




1940, 1944–1953,
Flag of the Estonian Socialist Soviet Republic,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1953–1991,
Flag of the Estonian Socialist Soviet Republic,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen



look also:
flag history of the soviet republics of the USSR

The
blue-black-white flag of Estonia was initially the flag of a scholar
fellowship, and was hoisted up for the first time in the year 1881, and
finally banned in 1896.
In context with the achievement of the independence from Russia the flag was
re-introduced in the year 1917, and confirmed with the constitution from the
4th of July in 1920.
There are many theories
to explain the meaning of the colours:
1.) The blue stands for loyalty and
trust, the black for the ancestors and the past and the white for the snow
and the future. Source: Flaggen-Atlas Erde;
2.) These are the colours of the
Finnish fraternal people, blue and white, supplemented by black to remind of
the dark time of serfdom. Source: unknown;
3.) Blue stands for the sky,
black for the land and white for the snow. Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt;
4.) Blue stands
for loyalty, the sky, the sea and the lakes, black for the oppression in the
past, the soil of the country and is the traditional color of the jackets of
the farm workers, white stands for the struggle for freedom, virtue, snow
and is the colour of the birch bark. Source: Nationalflaggen der Welt.
In the
years of the soviet occupation (1940 and 1944–1990) was in use until 1953 a
single colour red flag, on it hammer, sickle and the initials of the country
in gold. In the year 1953 was introduced a new soviet flag, which was
officialliy
in use even until 1991, although the old flag was already allowed since
1988. By the Estonian historian Indrek Kiverik was detected, that
international and partial even in Estonia, is in use a much to dark blue at
the styling of the estonian flag. The representation in the
Flag-Encyclopaedia was amended from there. Here is a Link to the Estonian
Reich Chancery,
where the coloring of the flag is given in the parameters of the
CMYK-spectrum. (=> click here)
Source:
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Alle Flaggen alle Staaten


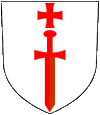
Coat of arms of Estonia,
Source:
Riigikantselei, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

1230–1237,
Blazon of the Order of the Sword Brothers (Livonian Order),
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

1237–1561,
Blazon of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights),
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

1629–1721,
Coat of arms of Livonia,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

The coat of arms of Estonia descents from the year 1918 and shows a golden shield with three among themselves grouped lions, surrounded by oak twigs. It is originally the coat of arms of the town Reval (Tallin), which is borrowed again from the coat of arms of the state Denmark. In the times where Estonia belonged to the Soviet Union was in use a soviet model, which equals the coat of arms of the Soviet Union. In 1989 they re-introduced the coat of arms of 1918. During the Second World War – in the time of the German occupation between 1941 and 1944 – Estonia officially had no own national emblems. It belonged to the Empire's Commissionership of Ostland, in which have been summarized the countries of the Balticum and parts of the today's northwest of White Russia (Belarus). The Estonain Legion, which voluntary fought on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union in the Second World War used as sleeve-insignia a golden shield with three black lions and above them the name of the country.
Source:
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Alle Flaggen alle Staaten,
Avantgarde für Europa

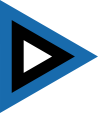
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
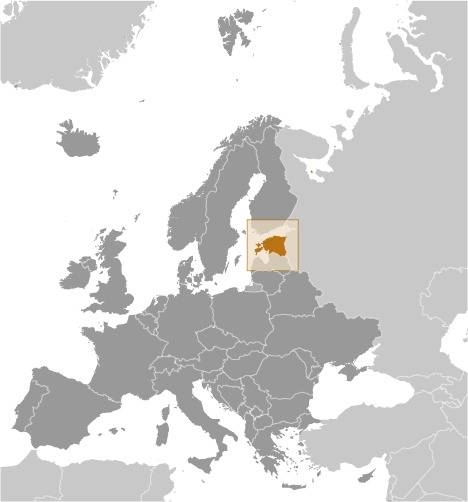
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
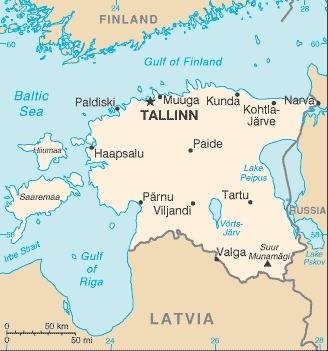
Source: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Baltikums:
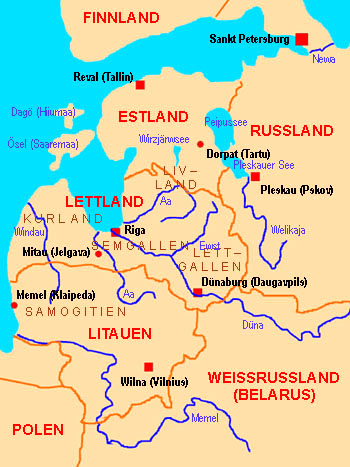
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: 17.505 km²
Inhabitants: 1.323.824 (2019), thereof 69% Estonians, 25% Russians, 3,8 % Ukrainians, White Russians (Belarusians), Finns, Tatars, Latvians, Poles, Jews, Lithuanians, and also 0,1% Germans
Religions: 13,6% Protestant, 12,8% Orthodox, 60% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 76 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Tallinn (Reval), 434.562 inh. (2019)
official Language: Estonian
other Languages: Russian
Currency from 1st of January 2011: 1 Euro (€) = 100 Cent
Currency to 31st of December 201: 1 Estonian Crown (ekr) = 100 Senti
Time Zone: GMT +2 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

2000 B.C. · settlement of the today's Estonia by the Estonians
1202 · establishment of the "Order of the Sword Brothers" in Duenamuende (today's Latvia)
1202–1230 · conquest of Courland, Livonia, Lettgallia, Semigallia and the southern Estonia by the Order of the Livonian Order, the northern Estonia becomes subjected by the Danish King Waldemar II.
1236 · defeat of the Order of the Sword Brothers against the Lithuanians
1237 · unification of the Order of the Sword Brothers with the Teutonic Order, Courland, Livonia, Lettgallia, Semigallia and the southern Estonia come as Livonian Federation with an own Master to the State of the Teutonic Order
1346 · the northern Estonia gets purchased by the Teutonic Order from Denmark and incorporated to the Livonian Federation of the Teutonic Order
1558–1595 · Livonian War, the Livonian Master of the Teutonic Order transforms Courland and Semigallia in a duchy as a Polish enfeoffment, Estonia becomes ceded to Sweden and partially to Denmark, Livonia and Lettgallia come directly to Poland
1621 · Sweden conquers Livonia
1629 · Livonia comes officially to Sweden
1710 · Nordic War, Russia conquers Livonia
1721 · Peace of Nystad, Livonia and Estonia come to Russia, Courland, Semigallia and Lettgallia remain at Poland, Estonia becomes an own Russian gouvernement (consists of the northern former Swedish part of Estonia)
1914–1918 · First World War: 1918 the German Empire conquers Livonia and Estonia
7th of November 1917 · bolshevist revolution in Russia, seizure of power by the Soviets
24th of February 1918 · Estonia declares its independence, the state of Estonia includes now the old Gouvernement of Estonia inclusive the north of Livonia
3rd of March 1918 · Russia capitulates towards the German Empire, Peace Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, recognition of the Estonian state by Soviet Russia
1924 · suppression of a communist coup d'état
23rd of August 1939 · German-Soviet non aggression pact, Estonia becomes a soviet sphere of interest and gets occupied by the Soviet Union
21st of July 1940 · proclamation of the Estonian Socialistic Soviet Republic (ESSR)
6th of August 1940 · inclusion of the ESSR into the Soviet Union, deportation of thousands of inhabitants
1939–1945 · Second World War: June/July 1941 conquest of Estonia by German troops, Estonia comes to the empire`s commissionership of Ostland, 20.000 Estonians fight voluntary in a Estonian Legion on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union, December 1944 conquest of Estonia by soviet troops, Estonia becomes once more ESSR and incorporated into the Soviet Union again, forcible russification, deportation of thousands of Estonians to Sibiria
1945–1988 · enforced immigration of Russians
1988 · nascence of the autonomy movement
30th of March in 1990 · proclamation of independence
1991 · the Soviet Union recognizes the independence of Estonia
1992 · new constitution
1994 · withdrawal of the Russian troops
2004 · Estonia becomes a member in the European Union
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Avantgarde für Europa

The name "Estonia" has its roots in the people of the "Estonians". They name themselves "Eestlased", what descents from the word "Aueist" and means "Coastal Residents".
Source:
Die Völker der Erde,
Atlas der wahren Namen

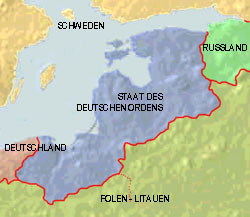
1410–1561
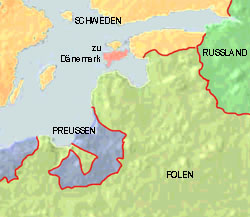
1561–1621
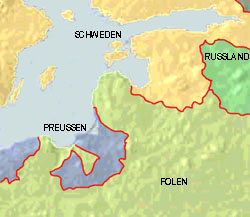
1621–1721
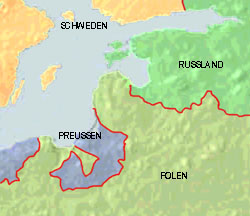
1721–1772
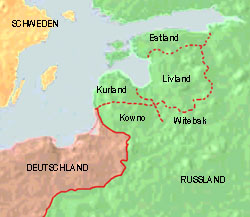
1815–1918
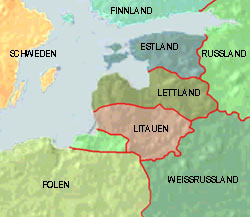
since 1991
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()

















































