mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Senegal
- presidial republic
- own name: République du Sénégal
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Regional Flags:
Casamance
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

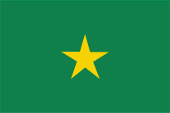
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






1958–1959,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1959–1960,
National flag of the Mali-Federation,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The today’s flag of Senegals was officially introduced on 19th of August in 1960, by other sources not until September 1960. It shows three vertical stripes in the pan-african colours green, yellow and red. In the yellow middle stripe is placed a green five-pointed star. It stands
• for the freedom of the african continent, for the hope for a better future and for peace
• for the sovereignty of the country
About the meaning of the colours exist different interpretations:
• green stands for the fruitfulness of the soil, yellow for the love to the fatherland and red for the blood, which was given for the independence
• green stands for the religions of the country (Islam, Christianity, pristine religions), yellow stands for richness in nature and prosperity, red for the live and fairness
On 25th of November in 1958 Senegal became an autonomous republic within the French Community (Communauté Française) and introduced initially a green flag with a yellow star. Since the 4th of April in 1959 Senegal formed together with the former French Sudan (Mali) the Mali Federation. This state became independent on 20th of June in 1960 and used a green-yellow-red vertical striped flag with the "Kanaga" (Mali Ideogram, stylized Black) in the yellow field. Two month later Senegal left the federation and became a sovereign state. Few times later the Mali Ideogram was removed from the flag and was substituted by a green star. The star should symbolize that Senegal is opened to all five continents.
The flag of the president has the same design like the national flag, but shows further the initials of the president in black, mostly ever one letter to both sides of the star.
The colours of the flag are probably not exactly defined. The following definitions can be found from time to time: Green = Pantone 361, Yellow = Pantone 116, Red = Pantone 186. The colours green, yellow and red are the Pan-African colours. The Pan-African-Movement had its beginnings perhaps in 1900, which wants to emphasize the common goals of all black people. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, which are used by many African and even American countries in their flags after independence, stands for the political unity of Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin, the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa, apply.
Source: Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


Coat of arms of Senegal,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of Senegal was introduced in December 1965. It shows a clefted shield. In the left half a golden lion on red ground – It stands for strength – in the right half a Baobab (carob tree) as a typical substitute of the flora of Senegal and in the lower part a green wave-line. It stands for the Senegal River the lifeline of the country. On the silvery banners the motto of the country in French language: "Un Peuple, Un But, Une Foi" → "One People, One Goal, One Faith".
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
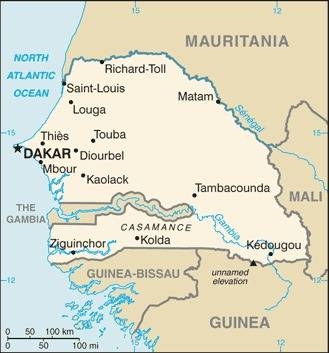
Source: CIA World Factbook
interactive Map:
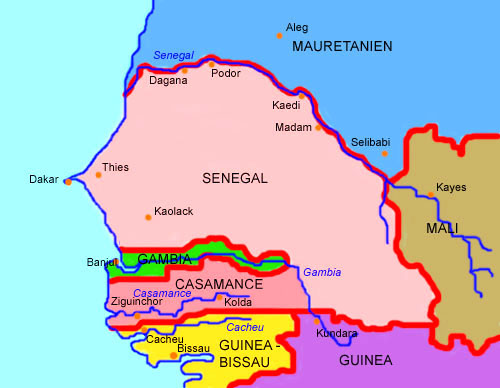
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 75.954 square miles
Inhabitants: 17.200.000 (2021), thereof 36% Wolof, 30% Fulbe and Toucouleur, 15% Serer, 4% Jola, 3% Mandinka, 0,3% French
Religions: 96,6% Muslim, 3,3% Christian (mostly Roman Catholic)
Density of Population: 227 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Dakar, 1.146.052 inh. (2013)
official Language: French
other Languages: Wolof, Fulbe, Mande
Currency: CFA-Franc (BCEAO) = 100 Centimes,
CFA = "Communauté Financière d’Afrique"
Time Zone: GMT
Source: Wikipedia (EN),
Wikipedia (DE)

500 B.C. · the Carthagian seafarer Hanno sails round Cape Verde
900 A.D. · evolution of local tribal states, e.g. the State of the Tekrur (Toucouleur) at the mouth of the Senegal River, the State of the Wolof in the west of the today’s Senegal, the State of Futa Toro (Fulbe) in the east of the today’s Senegal
11th century · islamization
14th–15th century · parts of the today’s Senegal belong to the Mali-State
1364 · Norman seafarers reach the Senegal River and sail around Cape Verde
1446 · the Portugese seafarer Diniz Fernandez sails around Cape Verde, in the afteryears establish Portugese merchants trading stations and bases southern Cape Verde (Beziguiche, Portudal, Rio Fresco and Joala)
ca. 1600 · Portugal withdraws from Cape Verde, the housing estates decay
1621 · the Netherlands establish on Goree Island (Ngor) near Cape Verde a base
1626 · France establishes near the mouth of Senegal River the base of Saint Louis
1638 · Saint Louis becomes protected by a fort
1640 · France establishes at the Senegal River the base of Podor
1672 · foundation of the "Compagnie de Sénégal"
1677 · France occupies Goree Island, the Dutchman become banished
1693 · United Kingdom occupies momentary the French bases at Senegal River
1697 · France establishes at the Senegal River the base of Madam
1758–1779 · United Kingdom occupies the French bases at Senegal River
1800–1817 · United Kingdom occupies the French bases at Senegal River
ca. 1830 · the Frenchmen invade the hinterland and establish further stations and bases at the coast, in the hinterland and on Gambia River
1854 · the French possessions between Senegal River, Cape Verde and the Gambia River become summarized to "Senegambia" and subordinated for the first time under a governor (General L. Faidherbe)
1857 · foundation of the town Dakar
1870–1883 · the military resistance in the hinterland becomes broken, the French troops move southern of Senegal River gradually eastwards to reach the Niger River in the today’s Mali, 1880 conquest of Bafulabe, 1881 conquest of Kita, 1883 conquer the French troops Bamako at Niger River
1885 · opening of a railroad line between Saint Louis and Dakar
1889 · border treaty with United Kingdom around the Gambia River
1895 · establishment of the Government General French West Africa
1902 · establishment of the colonial federation of French West Africa consisting of:
1st Mauritania – French Sudan – Niger Colony – Uppervolta
2nd Senegal
3rd Dahomey
4th Ivory Coast
5th French Guinea
1939–1945 · Second World War, Senegal is initially subordinated to the with the German Empire allied French government in Vichy
25th of November 1958 · Senegal becomes after a referendum no independent state but an autonomous republic within the French Community (Communauté Française)
4th of April 1959 · Senegal unites with the former French-Sudan (Mali) to the Mali-Federation within the French Community
20th of June 1960 · Senegal quits the Mali-Federation and becomes an independent state
1960–1980 · rule of the President Léopold Sédar Senghor
1963 · Senegal becomes a presidial republic, Senghor takes also over the function of the premier
1965 · extensive agreement about cooperation with Gambia
1966–1976 · single party system
1980–2000 · rule of the President Abdou Diouf
1982–1989 · Senegal and Gambia are connected in the Senegambia Confederation (joint military, economic and financial policy)
1989 · military quarrels with Mauritania
1990–1993 · Casamance-Conflict, the region of Casamance in the south of Senegal trys to separate from Senegal
1995 · once more battles in the Casamance
2000 · once more battles in the Casamance, strained relations with Mauritania
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Wikipedia (D)

The name of the country "Senegal" has its roots in the Senegal River. He is the lifeline of Senegal and its valley was the cradle of culture of this country. Senegal means in the language of the Wolof "the navigable".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()











