Palästina |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Palästina |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4   |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge der Fatah – flag of Fatah, Quelle/Source: MrPenguin20, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge der Hamas – flag of Hamas, Quelle/Source: Guilherme Paula, Oren neu dag, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1916–1927, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
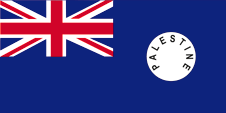 |
1929–1948, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2 Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
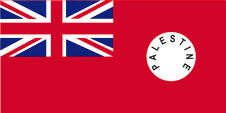 |
1927–1948, Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
| Der Farbenvierklang von Grün, Weiß, Schwarz und Rot ist ein speziell arabisches Farbsymbol, die Panarabischen Farben. Diese Farben wurden während des 1. Weltkriegs, bei der Loslösung des Königreichs Hedschas vom Osmanischen Reich, durch den Scherifen Hussein von Mekka – aus dem Geschlecht der Haschimiten – als Farben der Arabischen Bewegung offiziell eingeführt. Als Vorlage diente die Flagge des Hedschas. Die Farben haben folgende Bedeutung: Rot ist die Farbe von Omar, dem zweiten Kalifen; Weiß steht für die Omajjaden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den fünften Kalifen Moawija I. zurückgeht; Grün steht für die Fatimiden, eine ismailitisch-schiitische Kalifendynastie, die auf den vierten Kalifen Ali zurückgeht; und Schwarz steht für die Abbasiden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den Kalifen Abbas I. zurückgeht. Rot ist außerdem die Farbe der Haschimiten, eine arabische Herrscherdynastie, die wahrscheinlich auf Haschim ibn Abd al-Manaf, den Großvater Mohammeds, zurückgeht. | The
colour quartet of four, green, white, black and red is a special Arabian
colours symbol, the Panarabian colours. This colours were officially
introduced by Hussein the Sheriff of Mekka – of the lineage of the
Hashemites – as colours of the Arabian Movement in the First World War
during the secession of the Kingdom of Hedjas from the Ottoman Empire. The
flag of Hedjas served as pattern.
The colours have the following meaning: Red is the colour of Omar, the
second calif; white stands for the Omajiades, a calif-dynasty, which
goes back to the fifth calif Moawija I.; green stands for the Fatimids, a
ismailitic-shiit calif-dynasty, which goes back to the fourth calif Ali; and
black stands for the Abbasids, a calif-dynasty, which goes back to the
calif Abbas I. Red is also the colour of the Hashemites, an Arabian
sovereign-dynasty, which probably goes back to Hashim ibn Abd al-Manaf, the
grandfather of Mohammed. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Palästinensische Autonomiebehörde – Palestinian National Authority: Wappen von Palästina – coat of arms of Palestine, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Wappen Palästinas, so wie es von der Palästinensischen Autonomiebehörde verwendet wird ist ein silberner Adler Saladins. Auf der Brust trägt er ein Schild mit den Farben der Flagge. In den Fängen des Adlers ein Spruchband mit dem Namen des Staates. | The coat
of arms of Palestine, like it is used by the Palestinian National Authority, is a silvery Eagle of Saladin. On the chest it carrys a
shield with the colours of the flag. In the claws of the eagle a banner with
the name of the state. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Altsteinzeit · menschliche Besiedlung 7. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · erste städtische Siedlungen (Jericho) 3. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Entstehung von Stadtstaaten, Besiedlung durch semitische Völker (Kanaaniter) 2. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Blütezeit der kanaanitischen Kultur, Einfluss der Hethiter und Ägypter 14. und 12. Jhd. v.Chr. · Besiedlung des Landesinneren durch Israeliten (Juden) und der Küste durch Philister 11. bis 7. Jhd. v.Chr. · Staat Phönizien an der Küste 10. Jhd. v.Chr. · Königreich Israel 926 v.Chr. · Teilung des Königreichs Israel in Israel und Juda 721 v.Chr. · Eroberung von Israel und Juda durch die Assyrer 597 v.Chr. · Eroberung von Israel und Juda durch die Babylonier 540 v.Chr. · Eroberung von Israel und Juda durch die Perser 332 v.Chr. · Eroberung von Israel und Juda durch die Griechen (Alexander der Große) 323 v.Chr. · Tod von Alexander, das Griechische Reich zerfällt in Einzelstaaten, die von ehemaligen Heerführern Alexanders (Diadochen) geführt werden, Israel und Juda kommen an Laomedon, den Diadochen von Syrien ca. 200 v.Chr. · Eroberung von Israel und Juda durch Ägypten 63 v.Chr. · Eroberung durch das Römische Reich, Bildung der Provinz Judäa ca. 5 v.Chr. bis ca. 30 n.Chr.* · Leben und Wirken von Jesus Christus, Ausbreitung des Christentums 70 n.Chr. · Zerstörung des jüdischen Staates durch das Römische Reich, Vertreibung der Juden 135 n.Chr. · Auftstand des Bar Kochba, die Provinz Judäa wird in Palästina umbenannt 395 · bei der Teilung des Römischen Reiches kommt Palästina an das Oströmische Reich (Byzanz) 614 · Eroberung durch die Perser 636 · Eroberung und Islamisierung durch die Araber unter Omar 1070 · Eroberung Palästinas durch die islamischen Seldschuken, christliche Heiligtümer werden geschändet, Christen werden verfolgt und dürfen das Land (z.B. Wallfahrten nach Jerusalem) nicht mehr betreten 1095 · Papst Urban II. ruft in Clermont-Ferrand zum Krieg gegen die Seldschuken auf mit dem Ziel der Eroberung und damit des freien Zugangs zum Heiligen Land Palästina 1096–1099 · 1. Kreuzzug, Eroberung Jerusalems und Palästinas, Gründung von Kreuzfahrerstaaten (1081 Königreich Kleinarmenien, 1098 Fürstentum Antiochia, 1098 Grafschaft Edessa, 1099 Königreich Jerusalem, 1102 Grafschaft Tripolis) 1146 · Eroberung der Grafschaft Edessa durch die Seldschuken 1147–1149 · 2. Kreuzzug zur Rückgewinnung der Grafschaft Edessa, Fehlschlag 1187 · Eroberung Jerusalems durch Saladin den Sultan von Ägypten und Syrien 1189–1192 · 3. Kreuzzug zur Rückgewinnung Jerusalems, militärische Teilerfolge, Jerusalem bleibt in Saladins Hand 1202–1204 · 4. Kreuzzug, Eroberung Konstantinopels, Gründung des Lateinischen Kaiserreichs (1204-1261), Jerusalem bleibt in Saladins Hand 1228–1229 · 5. Kreuzzug, der deutsche Kaiser Friedrich II. erreicht 1229 durch Verhandlungen die Übergabe Jerusalems an die Christen 1244 · Eroberung Jerusalems durch die islamischen Sultane von Mossul (Zengiden) 1248–1254 · 6. Kreuzzug, Kämpfe in Ägypten und Tunis, Fehlschlag 1250 · die Mameluken übernehmen die Macht in Ägypten und Palästina 1270 · 7. Kreuzzug, Fehlschlag 1291 · die letzten Festungen der Kreuzfahrer werden erobert (Tortosa, Beirut, Sidon, Tyrus, Akkon) 1517 · Eroberung des Reiches der Mameluken (Ägypten, Palästina, Syrien) durch das Osmanische Reich 16. Jhd. · Einwanderung von Juden 1831–1840 · Mehmed Ali von Ägypten besetzt Palästina 1862 · Herausbildung des Zionismus als jüdische Nationalbewegung, daraufhin Einwanderung von Juden 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg, Palästina wird zwischen 1916 und 1918 von britischen Truppen von Süden her erobert, die ehemals Osmanischen Besitzungen in Arabien werden zwischen Saudi-Arabien, Großbritannien und Frankreich aufgeteilt 1917 · Balfour-Deklaration – Großbritannien beansprucht große Teile des Osmanischen Reiches nach dem bevorstehenden Kriegsende, und erklärt sich mit der Bildung einer „nationalen Heimstätte“ für die Juden in diesem Gebiet einverstanden 1920 · der Vertrag von San Remo spricht Großbritannien Palästina, Transjordanien und Irak als Mandatsgebiete des Völkerbundes zu 1922 · Palästina (einschließlich Jordanien) wird britisches Völkerbundsmandat 1923 · Jordanien wird als Emirat Transjordanien abgetrennt 1929 · blutige Auseinandersetzungen zwischen Arabern und Juden 1936 · nach jahrelanger starker jüdischer Einwanderung und keinerlei Reaktion der britischen Mandatsmacht, und keinerlei Garantien für Unabhängigkeit eines arabischen Palästina kommt es zu einem Arabischen Nationalaufstand 1939 · Niederschlagung des letzten arabischen Widerstands, Großbritannien beschließt die Errichtung eines arabisch-jüdischen Staats innerhalb von zehn Jahren 1942 · Zionisten fordern in New York die Bildung eines jüdischen Staats in Palästina 29.11.1947 · VN-Beschluss über die Bildung eines jüdischen Staates (Israel) und eines arabischen Staates (Palästina) auf dem Territorium des Mandatsgebietes Palästina →Ablehnung durch die Araber → Bürgerkrieg 14.05.1948 · das britische Mandat für Palästina endet, Proklamierung des jüdischen Staates Israel 1948–1949 · israelisch-arabischer Krieg, Annexion von 6.700 km² arabischen Territoriums durch Israel, Vertreibung der dort ansässigen arabischen Bevölkerung, die Palästinenser verzichten auf die Proklamation eines arabischen Staates, da er die Anerkennung der Teilung des Landes und der israelischen Annexionen bedeutet hätte 1950 · "Rückkehrgesetz", alle Juden die sich in Israel ansiedeln erhalten sofort die Staatsbürgerschaft, 1,7 Millionen Juden kommen ins Land 24.04.1950 · Transjordanien übernimmt die Verwaltung des Westjordanlands und nennt sich jetzt Jordanien, Ägypten übernimmt die Verwaltung des Ghazastreifens 29.10.1956 · israelische Aggression gegen Ägypten, Besetzung der Halbinsel Sinai und des Ghazastreifens → Intervention der USA, der Sowjetunion und der VN 25.12.1956 · die israelischen Truppen müssen den Sinai räumen, Stationierung von VN-Tuppen 08.03.1957 · die israelischen Truppen müssen den Ghazastreifen räumen, Stationierung von VN-Tuppen 1967 · Abzug der VN-Truppen 05.06.1967 · Israel greift Ägypten, Syrien und Jordanien an und besetzt innerhalb von sechs Tagen ("Sechstagekrieg") die ganze Sinaihalbinsel, den Gazastreifen, das Westjordanland, Ostjerusalem und die syrischen Golanhöhen 06.10.1973 · Ägypten und Syrien greifen Israel zur Rückgewinnung der besetzten Gebiete erfolglos an (Jom-Kippur-Krieg) 1988 · Jordanien verzichtet auf das Westjordanland 13.09.1993 · Abkommen zwischen Israel und der PLO, Abzug der israelischen Truppen aus dem Gazastreifen und Jericho, Herstellung einer begrenzten lokalen palästinensischen Selbstverwaltung 1994 · Errichtung erster palästinensischer Selbstverwaltungen in Jericho und im Gazastreifen 1995 · Teilrückzug der israelischen Truppen aus dem Westjordanland, palästinensische Selbstverwaltungen in weiteren Städten 1996 · Wahl des palästinensischen Autonomierates mit einem Präsidenten an der Spitze 2007 · Kämpfe zwischen den Palästinenser-Fraktionen Hamas und Fatah, die Hamas erobert den gesamten Ghazastreifen und beansprucht die Führung Palästinas 07.10.2023 · die Hamas überfällt aus dem Ghazastreifen heraus das umliegende israelische Gebiet und überzieht die Region mit religiös aufgeladenem Terror, binnen zwei Tagen erkämpft Israel die Kontrolle über seine Gebiete zurück und bekämpft in den folgenden Wochen Strukturen der Hamas im Ghazastreifen |
| * Die christliche Zeitrechnung wurde durch Dionysius Exiguus (ca. 470 – ca. 550) festgelegt, einem in Rom lebenden skythischen Mönch. Er führte, mittlerweile Abt geworden, seit dem Jahre 525 die christliche Zeitrechnung ein. Bei der Aufstellung von Ostertafeln im Jahre 532 rechnete er als Ausgangspunkt vom „Jahr von der Menschwerdung des Herrn“ an. Dabei unterlief ihm ein Fehler, der erst in der heutigen Zeit bemerkt und nicht mehr korrigiert wurde. Jesus Christus wurde tatsächlich 3 bis 7 Jahre vor dem "Jahr Null" geboren. |
| Oldest
Stone Age · human settlement 7th millenary B.C. · first urban settlements (Jericho) 3rd millenary B.C. · nascence of Town States, settlement by Semitic people (Canaanitans) 2nd millenary B.C. · flowering period of the Canaanitan culture, influence by the Hittites and Egyptians 14th und 12th cent. B.C. · settlement of the inland region by Israelits (Jews) and of the coast by Philistines 11th bis 7th cent. B.C. · State of Phoenicia on the coast 10. cent. B.C. · Kingdom of Israel 926 B.C. · division of the Kingdom of Israel in Israel and Judah 721 B.C. · conquest of Israel and Judah by the Assyrians 597 B.C. · conquest of Israel and Judah by the Babylonians 540 B.C. · conquest of Israel and Judah by the Persians 332 B.C. · conquest of Israel and Judah by the Greek (Alexander the Great) 323 B.C. · death of Alexander, the Greek Empire disintegrates in individual states which are lead by former army leaders of Alexander (Diadochi), Israel and Judah come to Laomedon, the Diadochos of Syria ca. 200 B.C. · conquest of Israel and Judah by Egypt 63 B.C. · conquest by the Roman Empire, formation of the Province of Judea ca. 5 B.C. to ca. 30 A.D.* · live and act of Jesus Christ, expansion of the Christianity 70 A.D. · destruction of the jewish state by the Roman Empire, expulsion of the jews 135 A.D. · revolt of Bar Kochba, Province of Judea becomes renamed in Palestine 395 · at the partition of the Roman Empire comes Palestine to the East Roman Empire (Byzantium) 614 · conquest by the Persians 636 · conquest and islamization by the Arabs under Omar 1070 · conquest of Palestine by the Islamic Seljuks, Christian sacrariums become violated, Christs become haunted and it is not allowed for them to come in the land (e.g. pilgrimages to Yerusalem) 1095 · Pope Urban II. appeal in Clermont-Ferrand to war against the Seljuks with the target of conquest and in this way free access to the Holy Land of Palestine 1096–1099 · 1st crusade, conquest of Yerusalem and Palestine, establishment of crusader's states (1081 Kingdom of Lesser Armenia, 1098 Principality of Antiochia, 1098 County of Edessa, 1099 Kingdom of Yerusalem, 1102 County of Tripolis) 1146 · conquest of the County of Edessa by the Seljuks 1147–1149 · 2nd crusade to win back the County of Edessa, failure 1187 · conquest of Yerusalem by Saladin, Sultan of Egypt and Syria 1189–1192 · 3rd crusade to win back Yerusalem, military partial successes, Yerusalem remains in the hands of Saladin 1202–1204 · 4th crusade, conquest of Constantinopel, foundation of the Latin Empire (1204-1261), Yerusalem remains in the hands of Saladin 1228–1229 · 5th crusade, the German Emperor Frederick II. gains in 1229 by negotiations the handover of Yerusalem to the Christs 1244 · conquest of Yerusalem by the Islamic Sultanes of Mossul (Zengides) 1248–1254 · 6th crusade, battles in Egypt and Tunis, failure 1250 · the Mamluks take over the power in Egypt and Palestine 1270 · 7th crusade, failure 1291 · the last fortifications of the crusaders become conquered (Tortosa, Beirut, Sidon, Tyrus, Akkon) 1517 · conquest of the Empire of the Mamluk (Egypt, Palestine, Syria) by the Ottoman Empire 16th cent. · immigration of Jews 1831–1840 · Mehmed Ali of Egypt occupies Palestine 1862 · development of the Zionism as jewish national movement, as a result of that immigration of Jews 1914–1918 · First World War, Palestine becomes conquered by British troops from southern direction between 1916 and 1918, the former Ottoman possessions in Arabia become partitioned between Saudi-Arabia, United Kingdom and France 1917 · Balfour-Declaration – United Kingdom demands large parts of the Ottoman Empire after the forthcoming end of the war and is in agreement with the idea of the creation of a "national homestead" for the jews in this area 1920 · the Treaty of San Remo assignes United Kingdom as a mandate of the League of Nations the countries Palestine, Transjordan and Iraq 1922 · Palestine (including Jordan) becomes a British mandate of the League of Nations 1923 · Jordan becomes separated es Emirate of Transjordan 1929 · bloody quarrels between Arabs and Jews 1936 · after a many years lasting strong jewish immigration and none reaction of the British mandate force and none guaranties for the independence of an Arabian Palestine arises an Arabian national rebellion 1939 · annihilation of the last Arabian resistance, British promise for a common jewish - arabian state within 10 years 1942 · Zionists claim in New York the formation of a jewish state within Palestine 29th of November in 1947 · UN-Resulution about the formation of a jewish state (Israel) and an arabian state (Palestine) on the area of the mandate territory of Palestine → dismissed by the Arabs → civil war 14th of May in 1948 · the British mandate for Palestine ends, proclamation of the State of Israel 1948–1949 · Israeli-Arabian war, annexation of 2.590 square miles of Arabian territory by Israel, expulsion of the here resident Arabian population, the Palestinians disclaim the proclamation of an Arabian state because this will imply the recognition of the partition of the country and the Israeli annexations 1950 · "Return Act", all jews which settle in Israel get immediately the citizenship, 1,7 millions of jews come into the country 24th of April in 1950 · Transjordan assumes the administration of the Western Jordan Land and calls itself now Jordan, Egypt assumes the administration of the Ghaza Stripe 29th of October in 1956 · Israeli aggression against Egypt, occupation of the Sinai peninsula and the Ghaza Stripe → intervention of the USA, the Soviet Union and the UN 25th of December in 1956 · the Israeli troops have to leave the Sinai, stationing of UN-troops 8th of March in 1957 · the Israeli troops have to leave the den Ghaza Stripe, stationing of UN-troops 1967 · withdrawal of the UN-troops 5th of June in 1967 · Israel attacks Egypt, Syria and Jordan and occupies within six days ("Six Days War") the whole Sinai peninsula, the Ghaza Stripe, the Western Jordan Land, East Jerusalem and the Syrian Golan height 6th of October in 1973 · Egypt and Syria attack Israel unsuccessfully to win back the occupied territories (Jom Kippur War) 1988 · Jordan disconnects itself from the Western Jordan Land 13th of September in 1993 · arrangement between Israel and the PLO, withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Ghaza stripe and Jericho, establishing of a limited local Palestinian self administration 1994 · establishment of first Palestinian Autonomy Administrations in Jericho and in the Ghaza Stripe 1995 · partial withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Western Jordan Land, Palestinian Autonomy Administrations in further towns 1996 · election of the Palestinian Autonomy Counsel with a President on the top 2007 · struggles between the Palestinian factions of Hamas and Fatah, Hamas conquers the whole Ghaza Stripe and claims the leadership in Palestine 7th of October in 2023 · Hamas invades the surrounding Israeli territory from the Ghaza Strip and covers the region with religiously charged terror; within two days, Israel regains control over its territories and fights Hamas structures in the Ghaza Strip in the weeks that follow |
| * The Christian chronicity was established by Dionysius Exiguus (ca. 470 – ca. 550), an in Rome living Scythian monk. He introduced since the year 525 – meanwhile he became an abbot – the Christian chronicity. At the listing of the Easter tables in the year 532 he calculated as starting position from the „Year of Incarnation of the Lord“. During this work he made a mistake which was realized not until the modern times and was not more corrected. Jesus Christ was really born 3 to 7 years before the "Year Zero". |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß |
| Der Name "Palästina" wurde dem "Judäa" um 500 v.Chr. von den Griechen gegeben. Er bedeutet "Philisterland". Die Palästinenser nennen es "Filastin". In der Bibel wird es "Kanaan" genannt. Die Christen nennen es noch "Heiliges Land", die Juden "Gelobtes Land". | The name "Palestine" was given by the Greek to the land "Judäa" about 500 B.C. It means "Country of the Philistines". The Palestinians call it "Filastin". In the bible it was named "Kanaan". The Christs call it further "Holy Land", the Jews "Praised Land". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |