Source, by: Flags of the World






since 2003,
Flag of the Defence Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



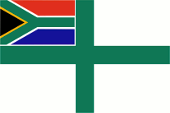
since 1994,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 2003,
Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 2003,
Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




"Vryheidsvlag",
Flag of the Boers,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The Union of South Africa was formed in 1910 through the unification of the following British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Orange River Colony (Orange Free State) and Transvaal.
Dutch Cape Colony:

1602–1660,
Flag of the Dutch East India Company,
Source, by:
commons.wikimedia.org




1660–1798,
Flag of the Dutch East India Company,
Source, by:
commons.wikimedia.org




1798–1806, Batavian Republic,
Flag of the Netherlands,
Source, by: Tom Lemmens, CC0,
via Wikimedia Commons



Union of South Africa:

1878–1931,
Flag of the High Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1910–1928,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)






1910–1912,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1912–1928,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1910–1928,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1910–1931,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1928–1982,
National, state, merchant flag and naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World




1928–1951,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1931–1953,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1947–1981,
Flag of the Defence Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1946–1951,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1951–1952,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



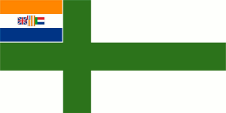
1952–1981,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1953–1961,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



Republic of South Africa:

1961–1984,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1982–1994,
National, state, merchant flag and naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World




1981–1994,
Flag of the Defence Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1981–1994,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1973–1994,
Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



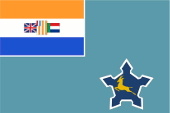
1982–1994,
Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1984–1994,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1994–2003,
Flag of the Defence Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1994–2002,
Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1994–2003,
Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The current flag of South Africa was introduced on 27th of April in 1994. It shows a horizontal green ypsilon with a black field on the mast, separated by a golden stripe; an upper red and a lower blue field are separated from the ypsilon by narrow white stripes. The colours of the flag appear to be defined, but are set out in a 1984 doctoral thesis by the University of Pretoria entitled "The National Flag of South Africa in Historical Perspective", as Pantone shades: green = pt 3415 c, yellow = pt 1235 c, red = pt 179 c, blue = Pantone Reflex Blue. There are two theories about the meaning of the colours:
• The flag is a combination of the colours of the ANC (black, green and yellow), the most important organization of black South Africans, and the colours of the "Vierkleur" (green, red, white and blue). The "Vierkleur" is the flag of the former Transvaal country, which represents the white South Africans here. The "Y" symbolizes the path of the united country into the future.
• The colors are intended to represent the historical territorial units of Cape Land, Natal, Orange Free State and Transvaal. The colors red, white and blue, the colors of the Dutch flag, are intended to indicate the white minority in the country. The black color represents the majority of the population.
The history of the country's flags can be divided into four periods. 1.) the period as a British colony "South African Union", without its own flag, completely subject to the British ensign system, until 1928. 2.) the period as a British colony "South African Union", but with its own flag, until 1961, 3.) the time of the "Republic of South Africa" as an independent, aspiring and economically very successful nation, until 1994, 4.) the time of today's South Africa.
Originally, before its subjugation by the British, South Africa consisted of Boer republics whose flags and heraldry were almost exclusively of Dutch origin. The Transvaal flag was the Dutch flag with a vertical green bar on the mast. It was called "Vierkleur" (four colours). The flag of the Orange Free State featured seven stripes of white and orange and the Dutch flag in the top corner. There were other Boer states, Goshen, Stellaland, Natal and the New Republic.
After the conquest of the Boer states by United Kingdom in the Boer War (1899–1902), the South African Union was formed in 1910 through the merger of the former Boer provinces and the British colonies, so that from that year on the flag of United Kingdom flew over the country. On land and also at sea, the individual citizen was represented by a "Red Ensign", and authorities and offices at sea were represented by a "Blue Ensign".
United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper orner.
From 1865, ships of colonial governments were allowed to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. The respective governments were to provide the corresponding bagdes. If the British Admiralty had granted a colony the appropriate permission, merchant ships and private seamen of these colonies were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the bagde. This was the case for the Union of South Africa from the very beginning. The "Red Ensign" with the badge was even allowed to be used on land as the national flag.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side. The Union of South Africa did not display a typical badge on the waving end of its Red and Blue Ensigns, but rather the escutcheon of the coat of arms granted to the colony in 1910. The shield was divided into quarters and showed in the individual fields: a woman with an anchor (Cape Province), two running wildebeests (Natal), an orange tree (Oranje Free State), a trek wagon (Transvaal).
The initially responsible British High Commissioner had his own flag. It was the usual flag for High Commissioners, the British Union Jack with the High Commissioner's badge in the middle, an abbreviation surrounded by a wreath with the British crown above it. The High Commissioner was responsible for South Africa, Bechuanaland, Basutoland and Swaziland. After the Statute of Westminster, South Africa became independent in 1931. In addition, from 1910 there was a Governor General, even after 1931, he was the representative of the head of state, the British monarch. That ended in 1961 when South Africa became a republic and the authority of a president was introduced, who also had his own flag.
On 31st of May in 1928 (according to other sources on 31st of March in 1928) a new, own flag was adopted for the Union of South Africa. It showed three horizontal stripes in orange, white and blue and three smaller flags in the centre of the white stripe: the Union Jack (for the former British colonies of Natal and Cape Land), the flag of the Orange Free State and the flag of Transvaal. The design of the flag was modelled on the flag of the Netherlands (also known as the "Prinsenvlag"), which is called in South Africa the "Van Riebeeck flag", as it was used by the early Dutch settlers. Originally, this flag was only flown on land and always alongside the Union Jack. However, this rule was cancelled in 1957. In 1982, the colours of the flag were revised as it was found that blue and orange were too dark and did not match the original descriptions. As a result, the colours were changed. This flag was abolished with the introduction of the current flag on 27th of April in 1994. Since August 2019, it has been illegal to fly this flag in South Africa. The offence of hate speech applies. The ban was imposed because white inhabitants of South Africa carried the flag at demonstrations in which they wanted to draw attention to their plight, which was characterised by dispossession and arbitrary killings.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Volker Preuß


since 2000,
Coat of arms of South Africa,
Source, by: wikimedia.org

1932–2000,
Coat of arms of South Africa,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

The current coat of arms of South Africa was introduced on 8th of April 28 in 2000. It shows a natural-colored shield with two Hottentots (Khoisan) touching each other with their hands. To the left and right of the shield are ears of grain and elephant tusks. Above the shield, crossed, a spear and a club. Above apears a secretary bird with its wings spread wide. He wears a stylized protea flower on his chest. Above the secretary's head is a golden arch with seven rays. Below, on a green banner, the country's motto in the Hottentot language in silver letters: !KE E:/XARRA//KE (→ "Different peoples unite"). The Hottentots are considered the country's original inhabitants because other black peoples and white settlers invaded their settlement area at the same time.
The previously used coat of arms was awarded by the British King George V. on 17th of September 17 in 1910. It showed a quartered shield and in the individual fields: a woman with an anchor (Cape Province), two running wildebeests (Natal), an orange tree (Oranje Free State), a trek wagon (Transvaal). Supporters were an antelope and a springbok and above the shield appeared the crest, a red lion with a bundle of blue and white rods in its fangs. Below the state motto in a banner: "Ex Unitate Vires" → "Unity makes strong". Since 1930, the shield has also rested on a green grass pedestal and in 1932 a helmet with red and white mantling and red protea flowers appeared above the shield.
Source:
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (DE),
Volker Preuß


since 2003,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1994–2003,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1957–1994,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1947–1957,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
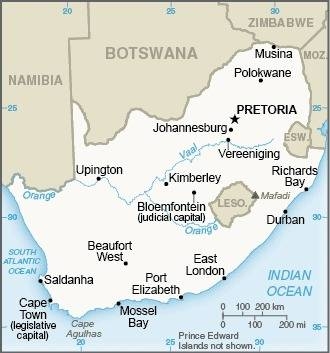
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 471.443 square miles
Inhabitants: 60.143.000 (2021), thereof 81% Blacks, 8% Mulattoes (Coloureds), 7% Europeans, 3% Asians
Religions: 60 % Protestant, 6,8 % Roman Catholic, 4,4 % Animist, 3,2 % Anglicans, 1,6 % Muslim, 11 % Non-Religious
Density of Population: 128 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Pretoria, 741.651 inh. (2011)
official Languages: Afrikaans, English, 9 Bantu Languages
Currency: 1 Rand (ZAR, R) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source: Wikipedia (DE),
CIA World Factbook

Antiquity/Middle Ages · in the today’s South Africa live Khoisanide nations (so named Hottentotts or Bushmen)
1488 · the Portugese seafarer Bartolomëu Diaz reaches the Cape of Good Hope
1497 · the Portugese seafarer Vasco da Gama sails around the Cape of Good Hope on the way to India
15th/16th century · immigration of black Bantu nations (Ndebele, Xhosa, Zulu, Sotho, Tswana, Swati, Venda, Tsonga ...)
1602 · the Netherlanders appropriate the land around the Cape of Good Hope (Kapland), settlement of Boers (farmer of Dutch and German descent, self-designation: Afrikaander)
1652 · Jan van Riebeeck founds the smallholding Kapstadt in mission of the Dutch East India Company
1806 · United Kingdom occupys Kapland
1814 · United Kingdom annexes Kapland officially, establishment of the British Cape Colony
1833 · abolition of slavery
1836–1885 · the Boers leave Kapland in long treks towards east and northeast and establish various Boer's republics (1838 Natal, 1854 Orange Free State, 1853 Transvaal, 1883 Stellaland, 1883 Goshen, 1884 New Republic ...), the British colonial power haunts the Boers
1845 · the British conquer Natal
1877 · the British submit the South African Republic (Transvaal)
1881 · anti-british revolt of the Boers in Transvaal, United Kingdom grants autonomy
1884 · the British occupy Walfish Bay (Walvisbaai, Walfischbucht) in South West Africa
1884 · re-establishment of the South African Republic in Transvaal
1885 · the British conquer Stellaland and Goshen, fused with British Betchuana Land
1888 · the British conquer the New Republic, fused with Transvaal
1899–1902 · Boers War, United Kingdom submit the Boer's States of Orange Free State and Transvaal, both become British colonies, chase and internment of the Boers, establishment of concentration camps for the Boers
1910 · United Kingdom joins the colonies Orange Free State, Transvaal, Natal and Cape Province to the South African Union, status of a British dominion
9th of July 1915 · South Africa occupys whole German South West Africa
1920 · Versailles Dictate, the German Empire loses all its colonies, German South West Africa becomes a Mandate Territory of the League of Nations under South African mandate
11th of December 1931 · Westminster Statute, United Kingdom grants the South African Union the independence in the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations
1939 · the attempt to stay neutrally in the Second World War fails
1939–1945 · participation in the Second World War
1945 · membership in the UNO
1948 · victory of the National Party in elections, official introduction of racial segregation
1960 · interdiction of ANC and PAC
31st of May in 1961 · the South African Union leaves the Commonwealth of Nations, proclamation of the Republic of South Africa
1976 · establishment of the homeland Transkei (for Xhosa)
1971 · establishment of the homeland Bophuthatswana (for Tswana)
1979 · establishment of the homeland Venda (for Venda)
1983 · new constitution, presidial system
1981 · establishment of the homeland Ciskei (for Xhosa)
1984 · new constitution
21.03.1990 · South Africa grants South West Afrika (Namibia) independence
01.03.1994 · South Africa cedes Walfish Bay to Namibia
27.04.1994 · new constitution, official abolition of the racial segregation, dissolution of the homelands, membership in the Commonwealth of Nations again
1997 · new constitution
2008 · nationwide xenophobic attacks by black South Africans
2014 · the party "Economic Freedom Fighters" (EFF), an extremely militant, radical and racist party of the black majority, enters parliament for the first time and becomes the third strongest force
2015 · nationwide xenophobic attacks by black South Africans
2018 · plans for land expropriation of white farmers without compensation are being discussed (since 1994, around 60 white farmers have been murdered every year; since 1994, around 1 million white citizens have left the country due to the conditions)
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
www.focus.de,
Wikipedia (EN)

The name "South Africa" describes first the geographic position of the country. It has its roots in the Boer's Republic of Transvaal, which 1853–1877 and 1884–1902 had that name.
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()














































![]()
