
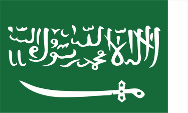
The flag of Saudi Arabia is a solid dark green coloured bunting and displays the shahada, the creed of Islam ("Allah il Allah, wa Muhammad rasul Allah" → "There is no God except the God; Muhammad is Allah's messenger") on one eighth of the total area of the flag, supplemented below by a white horizontal sword, with the tip of the sword pointing towards the end of the shahada. The front and back of the flag must be normally legible from both sides. In its current design, the flag of Saudi Arabia was officially introduced on 15th of March in 1973, the first time precise design provisions were established. The colour green is defined as Pantone 2427 C. Apparently the flag was changed a little in 1981 (sources are not clear). The shape of the sword was changed from a scimitar to a straight sword with a simple hilt and there were apparently also small changes in the typeface, which can still be found in different forms today. Between 1938 and 1973, some flags of Saudi Arabia showed two crossed swords, from 1946 on royal flags only. The Sauds' flag had a narrow white stripe on the mast-side in Nedjd and in Saudi Arabia to 1938. The Shahada filled the flag until 1973. After that, it was stipulated that it would only cover one-eighth of the flag's cloth. The flag of Saudi Arabia enjoys special prestige because of the revered Shahada, which may never be set at half-mast and may not be arranged vertically. Even carrying it in the hand, folding it, printing it on packages (which are then thrown away) is considered problematic. Recently, there have been considerations to create an additional national flag, which should be designed differently so that it can be handled more easily, e.g. at sporting events. The colour green was the colour of the Prophet Mohammed's coat. At that time, it was sometimes customary (also in Europe) to use items of clothing as flags. This was also the case with Mohammed's coat. The colour of the mantle thus very quickly became the colour and flag of Islam, and specifically the colour of the Fatimids, an Ismaili Shiite dynasty of caliphs dating back to the fourth caliph Ali, and Fatima, the daughter of Mohammed. In the 18th century, Ibn Abd al-Wahhab (1720-1792) founded an Islamic Sunni movement later named after him, the Wahhabis. He proselytised in Nedshd, and from 1745 gained great influence over the Saud family, the rulers of the Emirate of Al-Darija. This family completely adopted the symbolism of the Wahabis (the colour green, the Shahada), so that this symbolism became the heraldry of the Kingdom of Nedshd in the 20th century, and later also of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The sword was added to the flag of the then Saudi emirate of Nedjd in 1906, according to other sources as early as 1902, and refers to the founder of the state of Saudi Arabia Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis (1880-1953). It symbolises the military triumphs of Islam, the Saud family and the Wahabis. It stands for justice and righteousness.
Source:
Wikipedia (AR),
Wikipedia (EN),
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Die Welt der Flaggen


Coat of arms of Saudi Arabia,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen

The coat of arms shows within a green shield – probably a tent – two white crossed swords and above that a white date palm tree. The crossed swords symbolize the unification of the boths landscapes Nadjd and Hedjas, as well as the determination to defend the Islam. The palm tree stands for patience and perseverance, represents the agriculture of the country and is the symbol for the oasis in the desert. The coat of arms was indeed introduced not until 1950 but counted palm tree and saber since ca. 1930 for the national emblem of Saudi Arabia. The shield is in practice frequently leaved out. There exist black-white and green-white portrayals of palm tree and swords and they are used as coat of arms.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
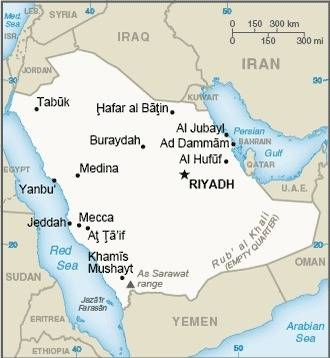
Source: CIA World Factbook
The Arabian Peninsula:
clickable Maps
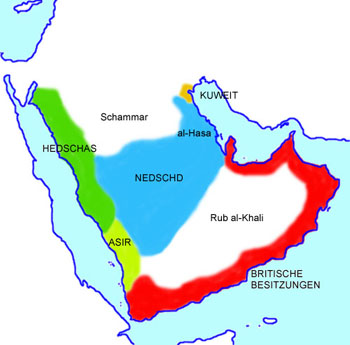
1920,
Map: Volker Preuß
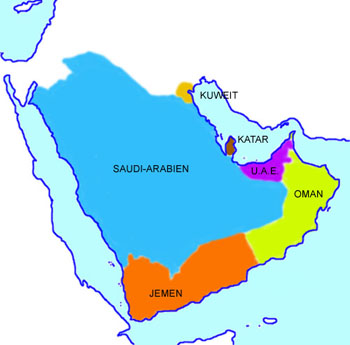
2006,
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 829.996 square miles
Inhabitants: 34.800.000 (2020), thereof 90% Arabs, 10% Turks, Persians, Indonesians, Indians, Africans
Religions: 73% Wahhabi Sunnis (Muslims), 12% other Sunnis (Muslims), 10% Shiites (Muslims)
Density of Population: 42 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Riad (Ar Rijad), 6.506.700 inh. (2023)
official Language: Arabian
other Languages: English, Arab dialects
Currency: 1 Saudi-Riyal (SAR, SRI) = 20 Qurusch = 100 Halala
Time Zone: GMT + 3 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

18th of September 1932 · founding of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by unification of the Kingdom of Hedjas with the Kingdom of Nadjd
1932 · war between Saudi Arabia and Yemen
20th of May 1934 · Peace of Taif between Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Italy and United Kingdom
1933 · the US-company Standard Oil gets the licence to open up the oil fields, in the afteryears
growing US-American influence
1934 · frontier treaty with Yemen
1939–1945 · Second World War, Saudi Arabia remains initially neutral, but United Kingdom and the USA belay air force bases in the country, joining to the war at the side of the allies on 1st of March in 1945, in the afteryears once more
growing US-American influence
1945 · Saudi Arabia becomes a member in the UNO and the Arab League
1953 · the USA stay durably in the country in their base Dhahran
1953 · death of King Ibn Saud, successor is his son Saud
1957 · annexation of the waters in the Golf of Akaba
1958 · territorial waters become expanded to 12 nautical miles
1962–1970 · during the civil war in Yemen Saudi Arabia supports the troops of the king against Egypt, which supports the (in the end victorious) troops of the republican revolution, bombardment of cities in Saudi Arabia by the Egyptian air force
1962–1970 · smoulding frontier war with the republican Yemen
1963 · abolition of slavery
1964 · expand of the military presence of the USA in the country, establishment of further US military bases
1964 · King Saud becomes dismissed, successor is his brother Faisal II.
1965 · big territorial exchange with Jordan
1965–1971 · partition of the neutral zone between Saudi Arabia and Kuwait
1973 · participation in the 4th Mideast War against Israel
1974 · frontier treaty with the United Arab Emirates
1975 · assassination of King Faisal II., successor is his brother Khaled Saud Ibn Abd Al Aziz
1979 · nationalization of the oil industries
1982 · death of Khaled Saud, successor is his son Fahd Ibn Abd Al Aziz
1983–1995 · partition of the neutral zone between Saudi Arabia and Iraq
1990 · Iraq occupies Kuwait, big deploy of US-American troops
1991 · Iraqi troops invade momentary on Saudi Arabian territory
1991 · partial withdrawal of the US-troops
1992 · frontier conflict with Qatar
1992 · once more frontier treaty with Yemen
1993 · first constitution
1993 · frontier conflict with Yemen
1995 · once more frontier conflict with Yemen
1995 · frontier treaty with Oman
1995 · big deploy of US-American troops
1996 · King Fahd hands over the governmental dealings to his half-brother Abdullah because of illness
2015 · death of King Abdullah, he is succeeded by his half-brother Salman, entering the civil war in Yemen
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

"Saudi Arabia" means the "Arabia of the Saud's". The name of the state has its roots in the founder of the state King Ibn Saud Abdul-Asis III., which established the Kingdom of Saudia Arabia in the year 1932. The familiy of the Saud's ruled since centuries in the Emirate of Al-Darija near the town of Riad in the heart of Nadjd. At the end of the 18th century they ruled already over the whole Nadjd and since 1926 they were even the Kings of Hedjas.
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()




































![]()
