Source, by: commons.wikimedia.org




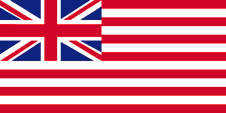
1858–1946,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)






1867–1946,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1868–1877,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1868–1877,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



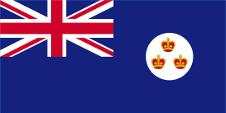
1877–1879,(?) uncertain,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



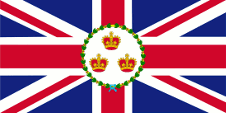
1877–1879,(?) uncertain,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



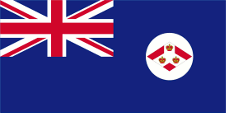
1879–1904,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1879–1904,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



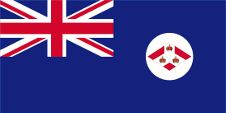
1904–1925,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



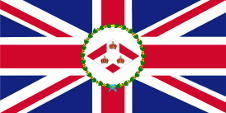
1904–1946,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



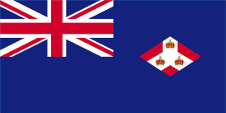
1925–1946,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




As the Colony of the Straits Settlements was created in 1826 by the die British East India Company, here was used its flag respectively the British Union Jack. The flags of the East India Company showed since the beginning of the 17th century white and red stripes, to differentiate better its ships from the other British ships. In the year 1867 the Straits Settlements became a British crown colony. For that was introduced a flag how it was usual at that times for British colonies. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
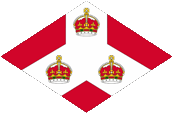
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The badge of the Straits Settlements was a red rhombus with a white shaft on which were layed down three crowns. That stood for the three places of Penang, Malacca and Singapore. On land, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At sea, the British citizen was thus provided with the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were allowed by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Volker Preuß


1868–1877,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1877–1879,(?) uncertain,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1879–1904,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World
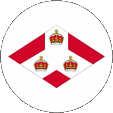
1904–1925,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World
1904–1925,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1874–1942,
Coat of arms of the Straits Settlements,
Source: Xavi Garcia, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

When the Colony of the Straits Settlements was created in 1826 by the die British East India Company, here was used its flag respectively the British Union Jack. The flags of the East India Company showed since the beginning of the 17th century white and red stripes, to differentiate better its ships from the other British ships. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, individual citizens and the authorities represented their status as citizens or bodies of the United Kingdom by using the Union Jack, known as the Union Flag. In the year 1867 the Straits Settlements became a British crown colony. For that was introduced a flag how it was usual at that times for British colonies.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for the Straits Settlements. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side. The badge of the Straits Settlements was a red rhombus with a white shaft on which were layed down three crowns. That stood for the three places of Penang, Malacca and Singapore.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World, Volker Preuß

clickable Maps
Straits Settelements ca. 1906:
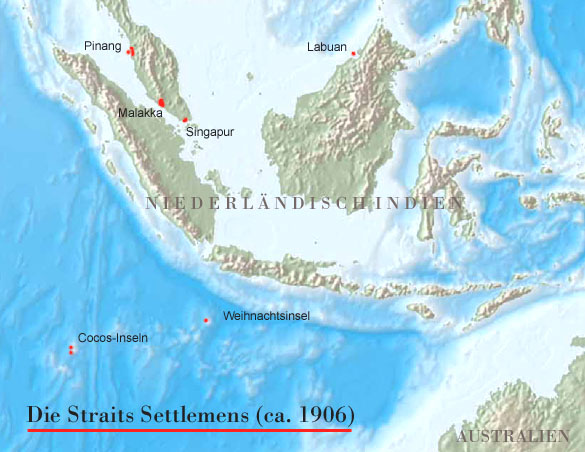
Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
Federal States of Malaysia:
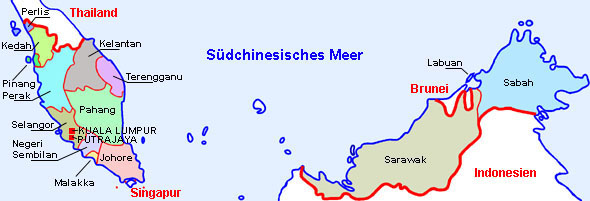
Map: Volker Preuß, to Malaysia? → click here
Malaya Peninsula:
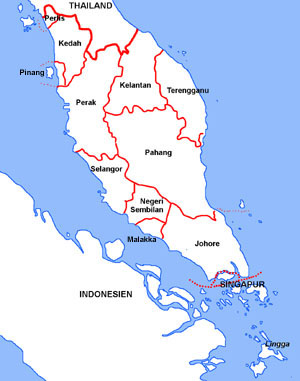
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 1.445 square miles (1887)
Inhabitants: ca. 536.000 (1887)
Density of Population: 371 inh./sq.mi. (1887)
Capital: Singapur, 172.993 inh. (1881)
official Language: English
other Languages: Malaysian, Chinese
Currency: 1 Sovereign = 4 Crown = 8 Half Crown = 10 Florin = 20 Shilling = 60 Groat = 240 Penny = 960 Farthing = 1 Pfund Sterling
Time Zone: GMT + 8 h
Source: RetroBib Retrobibliothek, Volker Preuß

1609 · the English seafarer William Keeling discovers the Cocos Islands
1641 · conquest of Malacca by the Netherlanders
1643 · the English seafarer William Mynors discovers Christmas Island
1685 · the British East India Company acquires the possession of Benkulen at the southern coast of Sumatra
1786 · the Sultan of Kedah calls for the British East India Company against Siam (Thailand), Francis Light occupies Penang Island and develops it to a base
1795 · conquest of Malacca by the British East India Company
1800 · the British East India Company acquires the mainland across from Pinang Island (Wellesley Province)
1818 · the Netherlanders conquer Malacca again
1819 · Sir Stamford Raffles from the British East India Company establishes on Singapore Island an agency
1824 · British-Dutch treaty of London for demarcation of the spheres of interest in the area of the Malaysian Archipelago, United Kingdom gets Malaya and the north of Borneo Island (the today’s Singapore, Malaysia and Brunei), the Netherlands get the today's Indonesia, exchange of territories: the British East India Company cedes Benkulen to the Netherlands, the Netherlands cede Malacca to the British East India Company
3rd of August 1824 · Sir Stamford Raffles and John Crawfurd purchase Singapore Island from the Sultan of Lingga for the British East India Company
14th of August 1826 · Singapore becomes joined with Penang and Malacca to the colony of the "Straits Settlements" under the supremacy of the British East India Company, seat of government is Gerorgetown on Pinang Island
1832 · the seat of government of the Straits Settlements becomes transfered from Penang to Singapore
1841 · the Sultan of Brunei has to accept the British supremacy over his country, Labuan Island is at that point in time a component of the Sultanate of Brunei
1857 · the Cocos Islands become appropriated by the British East India Company
1858 · the administration of the Straits Settlements becomes handed over to British India
1st of April 1867 · the Straits Settlements become a British crown colony
1870 · the administration of the Cocos Islands becomes handed over to the British Governor of Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1873 · the British East India Company becomes dissolved
1886 · the Cocos Islands become annexed to the Straits Settlements
1888 · United Kingdom establishes its protectorate over the Sultanate of Brunei
1888 · Christmas Island becomes appropriated by United Kingdom and affiliated to the Straits Settlements
1906 · Labuan becomes separated from the Sultanate of Brunei and affiliated to the Straits Settlements
1912 · Labuan becomes excluded from the Straits Settlements
1942–1945 · the Straits Settlements are occupied by Japanese troops during the Second World War
1st of April 1946 · the end of the Straits Settlements: Penang and Malacca become affiliated to the Malay Union (Malaya), but Singapore becomes an own British crown colony, the Cocos Islands and Christmas Island become annexed to Singapore, Labuan comes to British North Borneo
1st of October 1958 · the administration of Christmas Island becomes transfered to Australia
31st of August 1963 · United Kingdom grants Singapore the independence
16th of September 1963 · proclamation of the Kingdom of Malaysia by confederation of the Malaysian Federation (Malaya) with the former British colonies Sarawak, Sabah (North Borneo) and Singapore, Brunei rejects the joining and remains at United Kingdom
9th of August 1965 · Singapore leaves the Federation of Malaysia
1982 · formation of the Federal Territory of Labuan
Source: Wikipedia (EN), World Statesmen
![]()