mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Soviet Union (USSR)
- from 1922 till 1991 existent socialistic state
- own name: Sovjetskij Sojus
• Prolog
• Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Other Flags
• Historical Flags
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• List of the Soviet Republics
• List of the Autonomous Soviet Republics
• List of the Autonomous Territories
• List of the Autonomous Districts
• List of historical Satellite States
• Origin of the Country's Name
The Soviet Union called itself officially "Union of the Socialistic Soviet Republics". It seems, it could be something like a confederation of diverse Soviet Republics. To think so was the intention, and some of the republics had even an own seat in the UNO. In reality it was one state with one citizenship, the heir of the Russian Empire under the leadership of the communist party. The enforcement of bolshevism, the socialistic policy of Lenin, whichts costs the lives of about 80 millions of human beings until 1991, was successful under the nations of the Russian Empire, by the promise of "autonomy" in endless individual "Soviet Republics". In reality the leaders and elites og that nations became killed later, and there remained only and from the beginning on the centralistic, communist and russian policy of Moscow.
Source: Volker Preuß


1955–1991,
State and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






The last used (to 1991) and well known flag of Soviet Union was created in November 1923, and was introduced on 31st of January in 1924 in context with the adoption of a new constitution for the USSR, and it became finally confirmed on 19th of August in 1955. It showed a single-coloured red bunting in ratio 1:2 and in the upper staff quadrant crossed hammer and sickle under a red, yellow bordered star. The first flag of Soviet Union still showed the coat of arms on a single-coloured red bunting. In the following variant the coat of arms was removed and in the upper staff quadrant were added hammer and sickle and star. The upper staff quadrant was further separated from the rest of the flag by a slender yellow stripe. The hammer represented the workers (proletariat) and the sickle the farmers, the star stood for the unification of all humans of all countries of the five continents under the idea of communism. All communist red flags of the world have their roots in during the French Revolution of 1789 and during the Paris Commune of 1870/1871 used red flags. The origin is to search in the blood flags of the blood courts of the middle ages. The particular soviet republics had their own flags, just as the autonomous republics, territories and districts.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen


1935–1991,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939






1950–1991,
Naval flag of the Border Patrol (Coast Guard),
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1932–1991,
Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1950–1991,
Flag for aux ships,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1950–1991,
Flag of the Minister of Defence,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1950–1991,
Flag of the High Commander of the Armed Forces,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1950–1991,
Flag of the Supreme Commander of the Navy,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)





1923–1924,
State and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1924–1936,
State and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1936–1955,
State and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1924–1935,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggen Europas




1924–1935,
Flag of the chairman of war council,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1924–1935,
Flag of the Supreme Commander of the Navy,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggen Europas




1924–1927,
Flag flag of the chief of admiral staff,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggen Europas




1924–1935,
Flag of a chief of fleet,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)





1956–1991,
Coat of arms of Soviet Union,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of Soviet Union was adoped – like the flag – on 31st of January in 1924 in context with the adoption of a new constitution for the USSR. It was at last changed marginally on 12th of September in 1956. It showed the by hammer and sickle covered globe over a rising sun and under a red star. It was surrounded by wheat ears which were bond by a red ribbon. On the ribbon in the fifteen languages of the USSR the saying "Proletarians of all countries unite!". The coat of arms symbolized very graphic the striven world power of communism.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen


1922–1943,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1943–1991,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

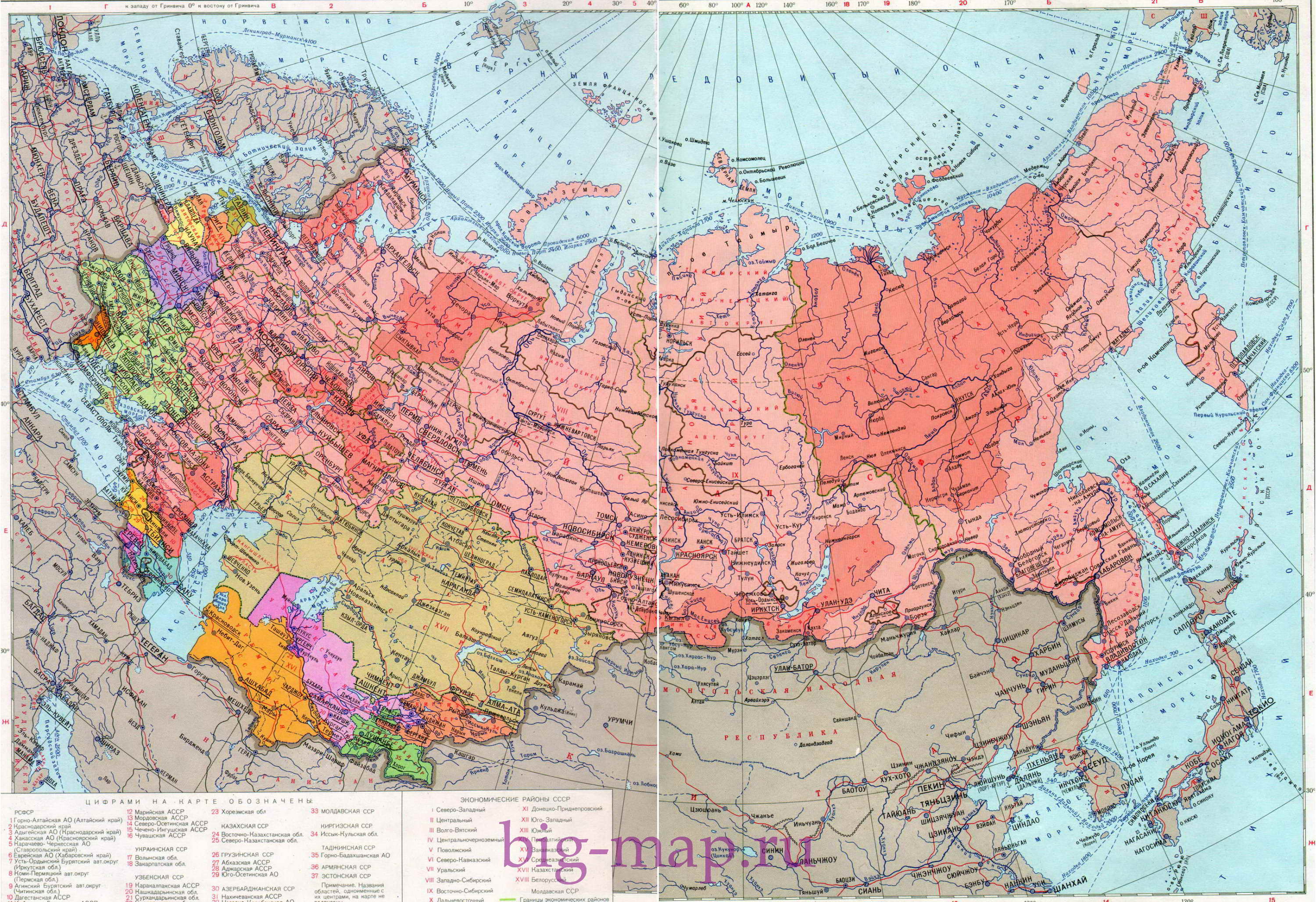
kukmor.livejournal.com, enlarge/click

Area: 8.649.500 square miles (1984)
Inhabitants: 276.300.000 (1984), thereof 50% Russian, 15% Ukrainian, 4,5% Uzbek, 3,5% Belorussian, 2,3% Kazakh, 2,2% Tatars
Density of Population: 32 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Moscow (Russ.: Moskva), 8.546.000 Ew. (1984)
official Language: Russian, Languages of the Soviet Republics
Currency: 1 Rubel (Rbl.) = 100 Kopeks
Time Zone: GMT + 3 h to + 13 h
Source: Länder der Erde

7th of November 1917 · bolshevist coup d’état ("October Revolution"), communists under W.I.Lenin seize the Power
20th of December 1917 · establishment of the Cheka (bolshevist secret police), beginning of the red terror
18th of January 1918 · the Bolshevists liquidate the free elected parliament of Russia in which they had only 175 of 707 seats
March/April 1918 · debarkation of foreign intervention troops in Murmansk (US-Americans, British, Frenchman) and Vladivostok (Japanese) to strike down the coup d’état of Lenin
25th of May 1918 · the anti-bolshevist Czechoslovak Volunteer Corps begins the fight against bolshevism near Samara
10th of July 1918 · appointment of a new constitution, Russia becomes the "Russian Socialistic Federative Soviet Republic (RSFSR, Soviet Russia)"
16th of July 1918 · Tsar Nikolaus II. and his whole family get murderd by Bolshevists
11th of November 1918 · end of the First World War, the German and Austrian troops withdraw from Soviet Russia
1918–1922 · civil war between civil, monarchistic and bolshevist forces under interference by foreign intervention troops, victory of the bolshevist forces, establishment of the Soviet power in whole Russia, this fact will cost the lives of ca 80.000.000 human beings in the direct scope of power of the Soviets until the year 1990
1919–1920 · establishment of soviet republics: Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Khorazm, Bukhara, Far Eastern Republic and Transcaucasian Federation
1919–1930 · formation of autonomous socialistic republics of nationalities within Russia (the today’s members of the Russian Federation)
April 1920 · Polish-Soviet Russian war
18th of March 1921 · Peace of Riga after the Polish-Soviet Russian war, Poland annexes large parts of Belarus (White Russia) and of the Ukraine
30th of December 1922 · foundation of the Soviet Union (USSR), combination of the Soviet Republics of Russia (RSFSR), Belarus (White Russia), Ukraine and of the Transcaucasian Federation
1922–1929 · establishment of further soviet republics: Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan
21st of January 1924 · death of W.I. Lenin, his policy costed until that point in time the lives of about 4 millions of human beeings, successor is J.W. Stalin
18th of September 1934 · joining to the League of Nations
5th of December 1936 · new constitution
1939 · German-Soviet non agression pact, the states of Balticum become a soviet zone of interest and become occupied by the Sowjet Union
1941–1945 · Second World War, the Sowjet Union can expand their borders far to the west
1945 · foundational member of the UNO
5th of March 1953 · death of J.W. Stalin, his policy costed until that point in time the lives of about 40 millions of human beeings, successor is N.S. Chrushtshov
7th of October 1977 · new constitution
11th of March 1985 · Michail Gorbachev becomes chief of state, starting of reforms
8th of December 1991 · Russia, Ukraine and Belarus (White Russia) declare themselves for sovereign and establish the „Commonwealth of Independent States” (CIS)
21st of December 1991 · joining of all former Soviet Republics of the USSR to the CIS (except Georgia), irrevocable end of the Soviet Union
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Russiatrek,
Die Völker der Erde,
Wikipedia (D)

1920–1991  Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic
Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic
1920–1991  Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
1940–1991  Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
1921–1991  Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
1940–1956  Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic
Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic
1925–1991  Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
1936–1991  Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
1940–1991 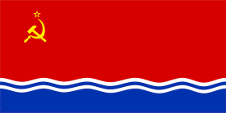 Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
1940–1991  Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
1940–1991  Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
1918–1991  Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
1929–1991  Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic
Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic
1922–1936  Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
1924–1991  Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
1918–1991  Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
1924–1991  Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
1919–1991  Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic

1924–1991  Nakhichevan ASSR
Nakhichevan ASSR
1921–1991  Abkhaz ASSR
Abkhaz ASSR
1921–1991  Adjarian ASSR
Adjarian ASSR
1919–1991  Bashkir ASSR
Bashkir ASSR
1923–1991  Buryat ASSR
Buryat ASSR
1921–1991  Dagestan ASSR
Dagestan ASSR
1922–1991  Yakut ASSR
Yakut ASSR
1936–1991  Kabardino-Balkarian ASSR
Kabardino-Balkarian ASSR
1958–1991  Kalmyk ASSR
Kalmyk ASSR
1936–1991  Komi ASSR
Komi ASSR
1936–1991  Mari ASSR
Mari ASSR
1930–1991  Mordovian ASSR
Mordovian ASSR
1936–1991  North Ossetian ASSR
North Ossetian ASSR
1920–1990  Tatar ASSR
Tatar ASSR
1936–1991  ASSR of Chechens and Ingush
ASSR of Chechens and Ingush
1925–1991  Chuvash ASSR
Chuvash ASSR
1961–1991  Tuvan ASSR
Tuvan ASSR
1934–1991  Udmurt ASSR
Udmurt ASSR
1932–1991  Karakalpak ASSR
Karakalpak ASSR
1920–1924  Turkestan ASSR
Turkestan ASSR
1921–1924 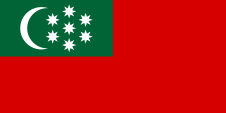 Mountain ASSR
Mountain ASSR
1923–1941  Volga German ASSR
Volga German ASSR

1923–1991 Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast
1922–1991 South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast
1922–1991 Adyghe Autonomous Oblast
1922–1991 Gorno-Altai Autonomous Oblast
1930–1991 Khakas Autonomous Oblast
1934–1991 Jewish Autonomous Oblast
1922–1991 Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast

1937–1991 Ust-Orda Buryat Autonomous Okrug
1937–1991 Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug
1930–1991 Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug
1930–1991 Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug
1930–1991 Evenk Autonomous Okrug
1925–1991 Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug
1930–1991 Koryak Autonomous Okrug
1929–1991 Nenets Autonomous Okrug
1930–1991 Taymyr Autonomous Okrug of the Dolgans and Nenets
1930–1991 Chukotka Autonomous Okrug

1920–1922  Far Eastern Republic
Far Eastern Republic
1921–1925  Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
1920–1925  Bukharan People's Soviet Republic
Bukharan People's Soviet Republic

The name "Soviet Union" was an abbreviation of the official name "Union of the Socialistic Soviet Republics". "Soviet" means "counsel", in the bolshevist sense a counsel which comes up spontaneously out of workers and farmers and which acts without democratic legitimation.
Source: Volker Preuß



![]()








































