mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag
![]()

























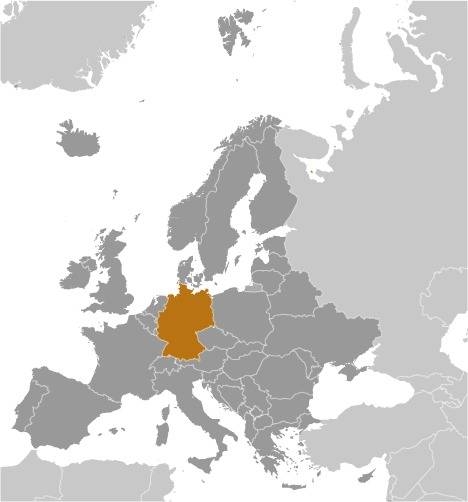
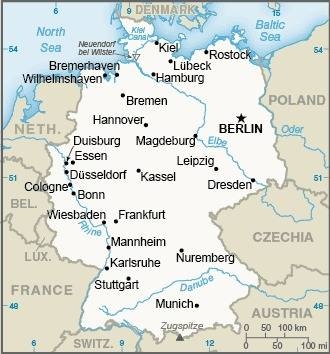
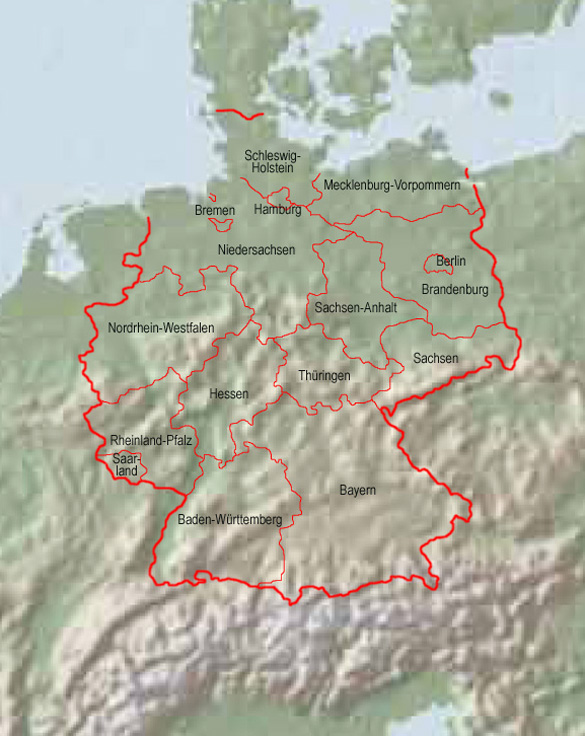
1200–1000 B.C. · Celtic settlement
600 B.C. · nascence of the Germanic culture
58 B.C.–455 A.D. · the territories left of Rhine River and south of the Danube River belong to the Roman Empire, to the provinces of Germania Superior, Germania Inferior and Raetia
395 · at the division of the Roman Empire the area of today's Germany comes to the Western Roman Empire
375 · Hun invasion, the beginning of the Great Transmigration (Migration Period), migration of the old Germanic tribes into the Roman Empire, moving up the Franks, Alemanni, Saxons, Bavarians and Thuringians, into central Germany, which is now deserted, migrate Slavs, this area is from now on called Germania Slavica
395 · onset of decline of the Western Roman Empire
476 · depose of the last Roman emperor Romulus Augustulus end of the (Western) Roman Empire
480–555 · the Merovingians become the rulers of all the Franks, formation of the Frankish Empire, subjugation of the Alemanni, Thuringians, Bavarians, Burgundians, conquest of Gaul to the Pyrenees and the Alps
751 · transfer of the power from the Merovingians to the Carolingians
768–814 · reign of Charlemagne, subjugation of the Saxons, enlargement of the Frankish Empire to the Iberian Peninsula, Italy and today's Hungary , the sphere of influence extends to the east to the Oder River and the Carpathian Mountains
800 · Charlemagne is crowned as Emperor
818–888 · disputes under the successors of Charlemagne, repeatedly divisions of the Empire (Treaty of Wirten [Verdun] 843, Meersen 870, Wirten [Verdun] 879 and Ribemont 880)
888 · Final division of the empire in a West Frankish Kingdom (France) and an East Frankish Kingdom (Germany) and Italy
900 · in the East Frankish Kingdom forme out five tribal duchies (Saxony, Bavaria, Swabia, Franconia and Lorraine), the beginning of the eastward expansion into Germania Slavica between the rivers Saale/Elbe and the Oder/Neisse, to 1400 annex of Mecklenburg, Brandenburg, Margraviate of Meissen, Silesia and Pomerania, the Teutonic Order conquers on behalf of the kings of Poland (East) Prussia, Pomerelles (West Prussia) and acquires the territories of today's Latvia and Estonia, confrontaions with the westward expansion of Poland
951 · the East Frankish King, Otto becomes king of the Lombards (Italy)
2nd of February 962 · the East Frankish King Otto I. is crowned as Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire (the empire includes the territories of today's Germany, Austria and Switzerland, Eastern France [Lorraine], the Netherlands, Eastern Belgium, Slovenia, Northern Italy and Bohemia) in the following centuries formes out none unified central governmented state (like France), but the reign of the Emperor must always hold back against the interests of the dukes, princes and cities, resulting of heritage divisions arise in the Holy Roman Empire up to 1.600 sovereign authorities and estates
987 · extinction of the Carolingians in the West Frankish Empire
1356 · Decree of the Golden Bull by Emperor Charles IV., the one constitutional document of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, setting of an electoral kingship by seven Electors (of Trier, Mainz, Cologne, the Palatinate, Saxony, Brandenburg and Bohemia), if the number of electors changed at times, the bull remained as valid to the end of the empire in 1806
1517 · Martin Luther spread his reforming protestant theses
1520–1530 · spread of the reformation
1618–1648 · Thirty Years' War in the German Reich as a confrontation between protestant and catholic contradictions and the influence of foreign powers (Sweden, France, Denmark), death of up to one quarter of the population, weakening of the power of the emperor
15th to 18th century · rise of Prussia as a great power in growing competition with the House of Habsburg (Austria)
1792, 1796, 1800 and 1805 · invasions of French revolutionary troops under Napoleon in the German Empire, the German Empire subjectes and becomes territorially transformed
1801 · all left-bank territories of the River Rhine ceded to France, and incorporated by this
1803 · German Mediatisation (Reichsdeputationshauptschluss), transformation of the territorial partition of the German Empire, ecclesiastical possessions become confiscated, old princely territories and free cities become confiscated or dissolved or annexed to old or new principalities, the number of sovereign authorities and territorial entities of the empire is thus reduced from 300 to 60
1804 · the German Emperor Franz II. assumes the title of "Emperor of Austria", and is thus emperor of an empire within his empire
12th of July in 1806 · Napoleon forces the creation of the Rhine Confederation, an alliance of sixteen southern and southwestern German states under French protectorate
1st of August 1806 · the states of the Rhine Confederation declare themselves sovereign and resign from the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation
6th of August in 1806 · Emperor Franz II. lays down the crown of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the empire ends, remaining or subsequent structures are the Rhine Confederation, Prussia and Austria
1813–1815 · war of liberation against Napoleon (Napoleon's defeat at 16th ot 18th of October in 1813 near Leipzig)
1815 · Congress of Vienna, reconstruction of Europe after the era of Napoleon, the ownership and the administrative partitions in the former German Empire become restored, but not the sovereignty of the ecclesiastical countries, their possessions become transferred to old or new principalities, the 39 remaining German states become organized in a loose association, the German Confederation
1833/1834 · founding of the German Customs Union (de facto Germany without Austria) under the leadership of Prussia
1848 · civil revolution, election of the Frankfurt National Assembly
1849 · suppression of the May Revolt, restoration of the pre-revolutionary situation, many Germans leave Germany and emigrate mostly to the U.S.A.
1864 · German-Danish War, Denmark cedes Schleswig
1866 · Prussian-Austrian War, or German War or Fratricidal War, defeat of Austria and its allies against Prussia and its allies, Prussia acquires Schleswig-Holstein, Hanover, Hesse-Kassel and Nassau, smashing of the German Confederation and Prussia forces the establishment of the North German Confederation
1866 · establishment of the North German Confederation
1st of July in 1867 · the North German Confederation gets a constitution, it becomes a federal state under the leadership of Prussia, chancellor becomes Otto von Bismarck
1870/1871 · Franco-German War
18th of January in 1871 · proclamation of the German Empire at Versailles, the king of Prussia was proclaimed as German Emperor, the constitution of the North German Confederation becomes transmitted with a few changes to the German Empire, France cedes the Imperial Province of Alsace-Lorraine to the German Empire, chancellor becomes Otto von Bismarck
1884 · Berlin Congo Conference, the German Empire develops its own colonial policy, and purchases until 1899 colonial possessions (Togo, Cameroon, German Southwest Africa, German East Africa, Kiaochow, Kaiser Wilhelm Land, Samoa, Nauru, the Mariana Islands, the Caroline Islands and the Marshall Islands)
1890 · resignation of Chancellor Bismarck
1914–1918 · First World War, an alliance of the German Empire with Austria-Hungary presses the German Empire on the side of the Central Powers into the war, because of the by Russia declared war on Austria-Hungary, after success and peace treaty on the eastern front, follows defeat is on the Western Front because of the intervention of the United States, in the German Empire arises the civic November Revolution, overthrow of the monarchy in the kingdom and in the federal states
9th of November in 1918 · proclamation of the Republic (also known as Weimar Republic, because the constitution was created in Weimar)
28th of June in 1919 · Dictate of Versailles, peace treaty between the German Empire and the Allies after the First World War, the German Empire is not involved in the negotiations and is – under the threat of occupation – forced to sign, the solely guilt on war of the German Empire becomes determined, the German Empire loses all its colonies and 27.000 sq.mi. of its territory, must disarm its army to 100.000 men, and suffer a 15 years enduring occupation of the River Rhine left-bank areas and pay gigantic reparations
1923–1925 · France and Belgium occupy the Ruhr Area
1929 · the global economic crisis and the results of the Versailles Dictate hit Germany hard, deterioration of the situation in the country, over the years escalation of the political situation, arise of extreme political left and right parties
1930 · governments of presidential cabinets of Imperial President Paul von Hindenburg rule by emergency decree, France withdrews from the Rhineland
30th of January in 1933 · Hitler's appointment to the Reichskanzler by the President of the Reich
24th of March in 1933 · The democratic parties in the Reichstag cede under the influence of extreme leftist actions and attacks the sovereignty of the parliament as the legislator to the government under the leadership of the National Socialists, the Weimar Constitution is suspended, the National Socialist rule becomes now dictatorial and installs a totalitarian national socialist one-party regime
1934 · the territorial structure of the countries in the German Empire becomes replaced by the districts of the Nazi Party, the countries become meaningless
1935 · plebiscite in the Saar Area, re-incorporation to the German Empire
1938 · annexation of Austria
1938 · annexation of the by an German majority populated Sudetenland
March 1939 · invasion of Czechia and establishment of the "Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia", re-incorporation of the Memel Area
1st of September 1939 to 9th of May 1945 · Second World War, end with the total defeat of the German Empire
23rd of May in 1945 · the government of the German Empire is arrested
1945 · the German Empire becomes occupied and split in occupation zones by the four Allies, large areas in the east will be subjected to Polish and Russian administration, the German population there becomes murdered or expelled
1945–1949 · between the Allies, United States, Great Britain and France on the one hand, and the Soviet Union on the other hand, arise tensions, because the communist Soviet Union and the West also, want Germany to integrate into their respective political and economic systems, a peace treaty with the German Empire does not come into existence, because there are exist no more German authorities
1945–1947 · the countries of the German Empire become restructured by the Allies, partially abolished (eg. Prussia on 25th of February in 1947), there were sometimes created entirely new countries (eg. North Rhine-Westphalia)
23rd of May in 1949 · the countries under the control of the Western Allies set up the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG)
7th of October 1949 · the countries under the control of the Soviet Union set up the German Democratic Republic (GDR)
1951 · Belgium, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg and the Netherlands, found the EEC (the later EU)
1952 · administrative reform in the GDR, the five countries will be abolished, initially become created 14 administrative districts
1961 · construction of the Berlin Wall, total isolation of the GDR against the FRG
5th of May in 1955 · the Allied Occupation Statute over the FRG ends, the country becomes partially sovereign
1957 · the FRG is a founding member of the European Economic Community (EEC)
1973 · the FRG and the GDR are members of the UN
Summer 1989 · departure and mass exodus from the GDR
Autumn 1989 · mass demonstrations in GDR, first for democratization, and later for the reunification of Germany
9th of November 1989 · fall of the Berlin Wall
1st of July in 1990 · monetary, economic and social union of the GDR and the FRG
3rd of October 1990 · annexation of the GDR to the FRG, in the former GDR the five countries become re-established
15th of March 1991 · come into force of the Two-Plus-Four Treaty, the former allies sede their jurisdiction
20th of June 1991 · the capital of the FRG becomes Berlin, the seat of government moves from Bonn to Berlin
1992 · treaty of Maastricht, the twelve countries of the EEC sign the "Treaty of the European Union (EU)"
1999 · German combat troops are the first time active abroad (Serbia) again
2002 · the FRG joins the Euro-zone (monetary union of states in the EU)
29th of June 2012 · the democratic parties of the parliament of the FRG cede under the influence of monetary problems of the Euro-zone, the sovereignty of the Parliament as the legislator in economic and financial questions to a 'Board of Governors' in Brussels
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß
![]()
Kindly supported by: A. Kortmann (D) und Königreich Hannover